* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 31 October: Supernovae and Neutron Stars
Survey
Document related concepts
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
White dwarf wikipedia , lookup
Nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary nebula wikipedia , lookup
Astrophysical X-ray source wikipedia , lookup
Main sequence wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear drip line wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
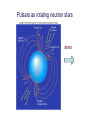
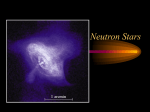
Supernovae and Neutron Stars Specific textbook sections • Evolution after the main sequence: Section 19.4 • White dwarf stars: Section 20.1 • Supernovae and neutron stars: Section 20.2 Core collapse of a massive star has two consequences • Massive explosion (1044 Joules) • Production of a neutron star Formation of a neutron star from stellar core • As core collapses, matter becomes compressed • Electrons and protons forced together e+p > n + nu (neutronization) • Core of the becomes a neutron fluid • Neutronization produces a burst of neutrinos • Neutron fluid in core becomes degenerate and rigid The physics of a self-gravitating neutron blob (neutron star) • Radius versus mass relation for neutron star • Notice size of neutron star • Masses extend above Chandrasekhar limit Theoretical prediction of the existence of a neutron star • The remnant after the explosion of a massive star • An object having the mass of the Sun (or more) but in an object with the diameter of Iowa City! • An equivalent to the Chandrasekhar mass (largest possible mass of a neutron star) • Do they exist? The problem of the Crab Nebula…the remnant of the supernova of 1054 AD Even today,something is powering the Crab Nebula, causing it to shine at x-rays 1968: The Discovery of Pulsars: Rotating Neutron Stars http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~pulsar/Education/Sounds/sounds.h tml Pulsar properties • • • • Highly regular pulse properties PSR0329+54, P=0.714519699726 sec PSR1633+24, P=0.4905065128003 sec What in nature could provide such a perfect clock? • Demo Pulsars as rotating neutron stars demo The Crab Nebula Pulsar http://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2002/0052/movies.html How many pulsars (neutron stars) are there in the sky? http://www.atnf.csiro.au/research/pulsar/psrcat Neutron stars: from exotica to numerous astronomical objects A final mystery…pul sar masses are nearly all AT the Chandrasekh ar Limit Periods and Period Derivatives for Pulsars