* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STARS and GALAXIES
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
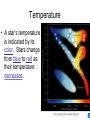
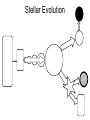
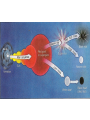
STARS and GALAXIES “Twinkle Twinkle Little Star, How I Wonder What You Are” Stars • A large ball of gas held together by gravity that produces tremendous amounts of heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer emit radiation (no light). Energy Production • Most of the tremendous amounts of energy produced by most stars is a result of nuclear fusion. Nuclear Fusion • The sun converts atomic nuclei into energy. • The energy of nuclear fusion of most stars is eventually radiated to space as types of electromagnetic energy. Classification System (ESRTpg.15) • Classification of stars is based on their temperature and luminosity in relation to our Sun. • Absolute Luminosity (brightness)Measures how bright a star is in relation to the sun, if all the stars were the same distance from the Earth. • Apparent Luminosity- The brightness we see when we look at the stars. Depends on the star’s distance and magnitude (strength). Temperature • A star’s temperature is indicated by its color. Stars change from blue to red as their temperature decreases. STAR TYPES • • • • • • • Main Sequence- average star (Sun) Giants- 10x size of Sun Supergiants- 100-1000x size of Sun White Dwarfs- small, planet sized Black Dwarfs- “dead” white dwarf, no energy Neutron Star- collapse, dense core of a star Black Hole- extremely dense remnant of a star Stellar Evolution Nebula