* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Properties of Stars
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Brown dwarf wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
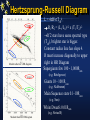
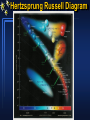
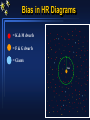
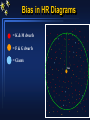
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Section 8.2 The story thus far Observed quantity Parallax, moving cluster Flux, F, at Earth, apparent magnitude (with d + inverse square law) Colour Index (B-V) (+ black body curve) Spectrum Binary stars (visual, spectroscopic, eclipsing) Calculated property Distances, d Luminosities, L (absolute magitudes) Temperatures, T Temperatures, composition, surface gravity, Luminosity class Masses, Radii But what about…… ages, how stars are born, how they shine, how they die? HR Diagram - introduction Make a plot of height vs weight for students in class B-ball players Supermodels Sumo wrestlers Height increasing upward - mass increasing to left Height Adults Children New-born babies Mass Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram A “Stellar Demographic Diagram” By turn century, astronomers were aware of a spectral sequence: OBAFGKM O stars are hot, luminous, most massive; M are stars cool, faint, least massive Originally, it was proposed that the spectral sequence was also an evolutionary sequence: start as hot O stars, use fuel, lose mass, cool to die as a dim M star 1905 - amateur astronomer, Hertzsprung, found a correlation between spectral type and absolute magnitude - but stars G and later showed a range in MV for same spectral type - brighter stars called “giants”. 1913 - established US astronomer, Henry Norris Russell, found same result. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram None available in sample Old type Spectral Type O B A F G K M N -4 Bright Stars 0 MV +4 +8 +12 T Henry Norris Russell’s first diagram: MV vs spectral type. Note: T increases to left and bright stars at the top. Band upper left to lower right is called the Main Sequence. It contains 8090% of all stars. White dwarfs at lower left. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram R Modern observer’s HR diagram L = 4R2Teff4 R1/R2 = (L1/L2)1/2 x (T1/T2)-2 If 2 stars have same spectral type (Teff), brighter star is bigger. Constant radius line has slope 4. R must increase diagonally to upper right in HR Diagram Supergiants few 100 - 1,000Rsun (e.g. Betelgeuse) Giants 10 - 100 Rsun (e.g. Aldebaran) Main Sequence stars 0.1-10Rsun (e.g. Sun) White Dwarfs 0.01Rsun (e.g. Sirius B) Modern theorist’s HR diagram Mass-Luminosity Relation Masses were obtained from observations of many binaries. Luminosities were obtained from parallax measurements. These are all main sequence stars Lower mass stars on main sequence Have cooler spectral types Main Sequence is a mass sequence Hertzsprung Russell Diagram Bias in HR Diagrams = K & M dwarfs = F & G dwarfs = Giants Sun Bias in HR Diagrams = K & M dwarfs = F & G dwarfs = Giants Sun Bias in HR Diagrams = K & M dwarfs = F & G dwarfs = Giants Sun Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Beware of the selection effects in the HR Diagram HR diagram of the stars nearest to the Sun. This is a proper sample of faint stars. Note that none of the rarer giant stars are within this volume of space. Luminosity Function of Stars Near to Sun Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Beware of the selection effects in the HR Diagram HR diagram of the brightest stars in the night sky. HR diagram of the stars nearest to the Sun. This is a proper sample of faint stars. Note that none of the rarer giant stars are within this volume of space. The number of giant and supergiant stars is small but they can be seen over vast distances.