* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download an object that moves around another object in space
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
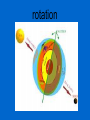
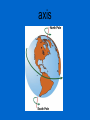
Earth, Moon, & Sun SOL 4.7 an object that moves around another object in space satellite a huge burning sphere of gas star the path an object, such as a planet, makes as it revolves around a second object orbit a group of objects in space that move around a central star solar system The motion of a planet as it turns on its axis. This takes 24 hours to complete. rotation The movement of any object in orbit, such as Earth moving around the Sun, which takes 365 ¼ days to complete revolution an imaginary line which runs through both poles of a planet axis a large object that moves around a star planet the different shapes the moon seems to have as it orbits around Earth phases I was a Greek astronomer who believed in the Earth-centered model of the universe (Geocentric). This means I thought the Earth was the center of the universe! Boy was I wrong! Aristotle I was an Egyptian astronomer who believed in the Earth-centered model of the universe (Geocentric). This means I thought the Earth was the center of the universe! I was wrong! Ptolemy I was a Polish astronomer who challenged the Geocentric model of the universe. I introduced the Suncentered model of the universe (Heliocentric). I believed the Sun was the center of the universe. Copernicus I was an Italian astronomer who believed the Sun-centered model of the universe (Heliocentric). I was even put in jail for a long time because of my belief! Galileo