* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Essay One - Physics & Astronomy
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
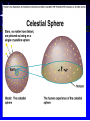
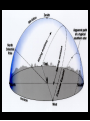
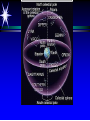
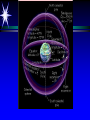
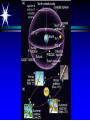
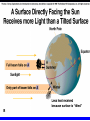
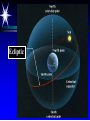
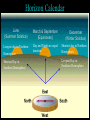
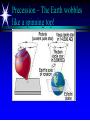
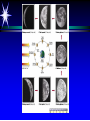
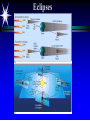
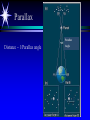
Astronomy 105 Student Information Sheet Class Syllabus Lab Syllabus Course Supplies Text Lab Manual Scantron 882-ES Flashlight with red filter In Search of E.T.'s Breath This is Astronomy …not astrology. A Sense of Scale The Earth- 13,000km=13x103km (8080 miles) Solar System- 6,000,000,000km=6x109km (4 x 109 miles) The Milky Way Galaxy-1018km(6x1018 miles) Local Group of Galaxies-1021km(6x1021miles) Universe-bigger than we can imagine. The Earth The Sun A Typical Galaxy 1 light year = 10,000,000,000,000 km 6,000,000,000,000 miles (10 trillion km) (6 trillion miles) Questions How many stars can one see on a clear night” Approximately 3000. What is the closest star to Earth? The sun On what horizon do stars rise? Set? Rise from east- Set in the west The Universe the totality of all space, time, matter and energy Astronomy the study of the universe Light Year the distance traveled by a beam of light in one year The Sky Calendar The sky is a master calendar. Day the time for one Earth rotation. Year the time for one Earth orbit around the Sun Month the approximate time for the Moon to orbit the Earth Solar Day and Sidereal Day Solar Day The time from one noon to the next. This is our 24 hr day. Sidereal Day A day measured by the slight shift of the stars positions from one evening to the next. This is roughly 23h, 56min. the Solar Day is approximately 4min. longer than the sidereal day. The Difference Between a Solar Day and a Sidereal Day. Synodic Month and Sidereal Month Synodic (Lunar) Month The time it takes the moon to complete one full cycle of phases, from one new moon to the next new moon) (29.5 solar days) Sidereal Month The time it takes the moon to complete one revolution around the Earth. (27.3 solar days) Sidereal Month and Synodic Month Tropical Year and Sidereal Year Tropical Year The time interval from one vernal equinox to the next. (365.242 mean solar days) The tropical year is the year our calendars measure. Sidereal Year The time required for the Earth to complete one orbit around the Sun, relative to the stars. (365.256 mean solar days – about 20 minutes longer than a tropical year.) Vernal Equinox Note: 360o = 24h Or 15o/h altitude - the angle of a star above the horizon The North Star, Polaris, is not the brightest star in the sky but remains in a fixed position in the sky. (near the North Celestial Pole) The angle of Polaris above your horizon is the same as your latitude in degrees. Questions Where are you if Polaris is directly overhead? Ans: North Pole Where are you if Polaris is on your horizon? Ans: Equator What is the altitude of Polaris in Nacogdoches? Ans: 31o 45’ 35.3’’= 31.7598o Longitude: -94 39 40.5 = -94.6613 Our Latitude View from the Equator View from the North Pole Circumpolar Stars Constellations Constellations are recognizable patterns of stars in the sky. (Based on stories and named in honor of them) There are 88 constellations. (e.g. Orion) The 12 constellations along the ecliptic on your star chart are called the Zodiac Constellations. Asterisms Asterism is a recognizable pattern of stars that is not one of the 88 constellations. For Example: The Big Dipper Asterisms developed as navigational tools for early seafarers. Asterisms can include parts of constellations (subsets), or can include two or more constellations (supersets). Seasons The path of our Sun across the celestial sphere is called the ecliptic. It is inclined 23½° with respect to the celestial equator. What causes seasons on Earth? Answer: The tilt of the Earth's rotational axis. Inclined Pole causes Seasons Ecliptic Horizon Calendar June (Summer Solstice) March & September (Equinoxes) December (Winter Solstice) Longest day in Northern Day and Night are equal duration. Shortest day in Northern Hemisphere Shortest Day in Southern Hemisphere. Hemisphere Longest Day in Southern Hemisphere. Motions of the Sun and Stars Daily Motion The rising and setting of the stars is caused by the Earth’s rotation about its axis. Annual Motion The Earth’s orbit around the Sun causes different stars to be visible at different times during the year. Precession Precession is the slow wobble of the Earth’s axis due to the influence of the Moon. Precession – The Earth wobbles like a spinning top! The Lunar Phases As the moon orbits the Earth, the moon goes through phases. Since the name of our moon is Luna, these are called Lunar Phases. Eclipses Why Don’t We Have a Lunar Eclipse Every Month? Ans: The orbit of the moon is also tilted!! Eclipses A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the sun and the earth. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes behind the Earth's shadow. Note: The shape of the Earth was determined by observing the shape of this shadow. 1st Quarter New Moon Full Moon 3rd Quarter Triangulation Triangulation A triangle of fixed baseline is narrower the farther away the object. BASELINE Measuring a Star’s Distance Parallax - the apparent change in the position of a star due to the motion of the Earth Nearby objects exhibit more parallax than remote ones. Stellar Parallax June Sun January Nearby Star Parallax Parallax Distance ~ 1/Parallax angle Angle End of Section...