* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DUPREE_SPLINTER
Survey
Document related concepts
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
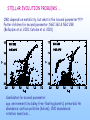
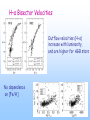
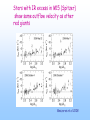
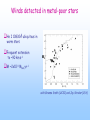
SLEUTHING MASS OUTFLOW FROM EVOLVED STARS Optical/IR Spectroscopy from the MMT, KECK II, and Magellan Andrea Dupree (SAO/CfA) Sz. Meszaros (SAO), Jay Strader (CfA), and Graeme H. Smith (UCSC) Cool Stars 15/Splinter: St. Andrews 21-25 July 2008 STELLAR EVOLUTION PROBLEMS …. CMD depends on metallicity, but what is the ‘second parameter’???? Poster children for second parameter: NGC 362 & NGC 288 (Bellazzini et al. 2001; Catelan et al. 2001) Candidates for second parameter: age, environment (including free-floating planets); primordial He abundance; surface pollution (helium); CNO abundances; rotation; mass loss….. FOCUS ON MASS LOSS … Mass loss is required theoretically on red giant branch to match CMD of clusters , but the mass presumably lost has ‘VANISHED’! Where and when does mass loss occur? What are the spectroscopic signatures of mass loss or mass flow? Omega Centauri Diagnostics of atmospheric motions Need to know where the diagnostic forms…. Contribution functions for a metal deficient giant star MMT/Hectochelle observations of globular clusters: M13, M15, & M92 240 fibres available to capture spectra in selected orders: H-α and Ca II (H&K) Ca K in M13 H-α in M92 Bisectors marked Sz. Meszaros et al. 2008, 2009 H–α Bisector Velocities Outflow velocities (H–α) increase with luminosity, and are higher for AGB stars No dependence on [Fe/H] Stars with IR excess in M15 (Spitzer) show same outflow velocity as other red giants Meszaros et al 2008 Ca K3 shows higher (accelerating) outflow than H-α Ca K3 H–α Helium 10830Ǻ observed with NIRSPEC/KECK II in M13 and metal-poor field giants Maps wind to higher levels of chromosphere Visible in warmer stars Reveals high velocities ~100 km s-1 Comparable to stellar escape velocity at 2Rstar AGB and RGB RHB stars with Graeme Smith (UCSC) and Jay Strader (CfA) [2008] Winds detected in metal-poor stars He I 10830Ǻ ubiquitous in warm stars Frequent extension to ~90 km s-1 MV M ~2x10-9 Msun yr-1 with Graeme Smith (UCSC) and Jay Strader (CfA) CONCLUSIONS H-α reveals increasing outflow velocity with luminosity. Ca K3 suggests accelerating expansion Outflows similar for metallicity [Fe/H] = –1.5 to –2.3 IR-excess giants not distinguishable from other giants in M15 No ‘superwind’ detected Mass loss (V ~ Vescape) discovered in rgb, rhb, agb objects with He I 10830Ǻ