* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
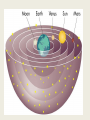
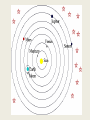
History of Astronomy: 1. Ancient view: Earth is the center of the solar system. This is called the geocentric model. The Sun and other planets revolve around Earth in circles. Sun E Jupiter Mars It gets much worse….. and worser….. Very weird! 2. Newer view: The Sun is the center of the solar system. This is called the heliocentric model. The Earth and other planets revolve around the Sun in circles. E Mars Sun Jupiter Kepler had to change the heliocentric model because it did not predict the planets’ positions accurately. 3. Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion Kepler’s 1st Law: The orbit of a planet or asteroid orbiting a star is an ellipse. The star is at one focus. This is also true for the Moon orbiting Earth. In this case, the Earth is at one focus. planet Sun x Earth x x Moon x Kepler’s 2nd Law: As a planet approaches the Sun, it moves faster. A planet moves fastest when it reaches its closest point: perihelion. As a planet moves away from the Sun, it slows down. It moves most slowly when it reaches its furthest point: aphelion. speeding up perihelion fastest (Jan 1st) Sun x x slowing down aphelion slowest (July 1st) Kepler’s 3rd Law: 1. The further a planet is from the Sun, the longer it takes to revolve. 2. The further a planet is from the Sun, the slower its orbital speed. orbital speed Period of Revolution (time for one year) MVEMJSUN (distance from Sun) MVEMJSUN (distance from Sun) Kepler did not know why his 3 laws were correct! Ex: 3 of the 4 Galilean moons of Jupiter: How do we know Saturn's rings are not one solid disk? 4. Newton explained why Kepler’s Laws were correct a. Gravity is the force that holds the planet’s in their orbits. The bigger the planet, the more the gravity. The farther a planet, the less the gravity b. Object tend to move in straight lines (inertia) The orbit of a planet is the result of a balance between gravity and inertia. Sun gravity planet inertia orbit