* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rise of the Renaissance Power Point
Survey
Document related concepts
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance painting wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
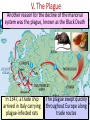
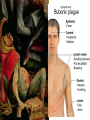
Western Europe emerged from the Middle Ages I. The Renaissance during an era known as the Renaissance From 1300 to 1600, Western Europe experienced a “rebirth” in trade, learning, & Greco-Roman ideas During the Renaissance, Europeans developed new ideas in art, gov’t, & human potential The Renaissance was a revival of learning based on knowledge from Classical Greece & Rome. This intellectual change has resulted in the Renaissance being viewed as a bridge between the Middle Ages and the Modern era. What changed during the Middle Ages that gave rise to the Renaissance? Trade & Cities? Government? Religion? Human Potential? Think…What was trade like during the Middle Ages? During the Middle Ages, trade was limited to the manor. Very little if any exchanges between manors existed. Think selfsufficient II. Trade & Cities during the Renaissance The Crusades increased European demand for luxury goods from Asia Italian merchants began meeting the demand for trade in Europe As a result, Italian cities & a wealthy middle class began to form in Italy The most important Italian city was Florence, where wealth from trade sparked the Renaissance In addition, the fact that Italians could look at the middle ruins ofclass the Roman Empire for inspiration, A new of The Medici family were bankers, & perfect wealthy bankers who used it merchants, made for the location for the skilled craftsmen Renaissance. their wealth to buy art gained lots of power (Patrons) Think…What changed during the Middle Ages that gave rise to the Renaissance? Trade & Cities? Government? Religion? Human Potential? Think…What was government like in the Middle Ages? During the Middle Ages, government was not centralized and therefore there was no peace and no stability III. Government During the Renaissance Kings were able to tax merchants & use their wealth to build armies & strong nations which hurt the power of the feudal lords From 1337 to 1453, England & France began a conflict called the Hundred Years War During the war, nationalism increased as people became loyal to their king & nation, rather than their lord During the Hundred Years War, new military weapons decreased the power of feudal lords & knights The discovery of Chinese gunpowder led to the development of cannons which helped armies penetrate castles The invention of the longbow allowed soldiers to shoot accurately up to 300 yards which decreased the importance of knights on horseback Think…What changed during the Middle Ages that gave rise to the Renaissance? Trade & Cities? Government? Religion? Human Potential? Think…What was religion like in the Middle Ages? The heavy reliance on religion gave way to the term “Age of Faith” During the Middle Ages, the only accepted religion in Europe was Roman Catholicism. The church was the only institution that provided stability. IV. Religion during the Renaissance In the late Middle Ages, the Pope & the Catholic Church lost some of its influence as a result of the losses to Muslim armies during the Crusades Despite having less influence, the Catholic Church was still an important part of peoples’ lives & the Pope remained important Think…What changed during the Middle Ages that gave rise to the Renaissance? Trade & Cities? Government? Religion? Human Potential? Think…What were common people expected to do during the Middle Ages? During the Middle Ages, most people were peasants. A hard life was lived where daily duties revolved around farming the manor. During the Middle Ages, peasants did not own land & had no options other than remaining loyal to a feudal lord & work within the manorial system As peasants left during the manor to seek new gave job The rise of trade the Renaissance opportunities, manor systems people optionsthe to leave the manorweakened & move to because were to do the was a cities tofew serve asleft merchants orwork. skilledThis artisans key factor behind the end to the feudal system. V. The Plague Another reason for the decline of the manorial system was the plague, known as the Black Death In 1347, a trade ship arrived in Italy carrying plague-infested rats The plague swept quickly throughout Europe along trade routes The Black Death The plague killed 25 million people in 5 years (1/3 of Europe’s population) The plague caused a labor shortage; those that survived could demand higher wages & more rights VI. Life during the Renaissance For those that survived the plague years, a greater desire to celebrate and enjoy life led people to believe that they should try new things Individuals became the center of attention during the Renaissance Social status was based on wealth & ability, not birthright A new way of thinking began during the Renaissance called Humanism Humanists studied the “classical” ideas of Greece & Rome & believed that individual human achievements should be celebrated What was expected of men & women in the Renaissance? The “ideal man” was well educated, smart, can dance, write poetry, & play music; (called a “Renaissance Man”) The “ideal woman” should have the same qualities as men but should not seek fame or political power (Renaissance women were better educated but had fewer rights than medieval women) The revival of trade in Europe helped bring an end to the Middle Ages & gave rise to the Renaissance The rise of cities brought artists together which led to new techniques & styles of art Increased trade gave rise Wealthy bankers & to Italian city-states & merchants wanted to a wealthy middle class show off their new status of bankers & merchants by commissioning art The most important Italian city-state was Florence; In this wealthy trade city, the Renaissance began Florence was home to the Medici family, the wealthiest & most powerful bankers in Europe The Medici used their wealth to commission art for themselves & to beautify Florence Florence under the Medici Lorenzo Cosimo Guiliano Medici Chapel The Medici paid tocommissioned build a massivethis Lorenzo de Medici painting from domed cathedral for Florence Botticelli of the Medici brothers as the three magi The Medici Palace New styles & techniques of Renaissance art ■Realism & emotion ■Classicism: inspiration from Greece & Rome ■Emphasis on individuals & interaction between people ■Geometric arrangements ■Perspective ■Using light Greek& shadows Renaissance Renaissance Artists Donatello ■ Donatello was the 1st great sculptor of the Renaissance – Donatello revived the classical (Greco-Roman) style of sculpture that were realistic & could be viewed from all sides – Donatello’s “David” was the 1st large, freestanding human sculpture of the Renaissance Michelangelo ■ Michelangelo was one of the most famous Renaissance artists: – He was a painter, sculptor, architect, & poet – His sculptures & paintings showed realism, detail of the human body, & expression to show personality & emotion Michelangelo sculptures “Pieta”& “David” are considered masterpieces Michelangelo’s greatest work is the 130 ft x 44 ft ceiling of the Sistine Chapel which shows Biblical images of amazing detail, power, & beauty Leonardo da Vinci ■ Leonardo da Vinci was a true “Renaissance Man” – He was a painter & sculptor whose art was known for incredible realism & emotion – He was also an inventor & scientist whose sketches reveal observations about human anatomy & new engineering technology His “Last Supper” shows Jesus’ last meeting with the 12 apostles before the crucifixion; the facial expressions, detail, emotion made it a masterpiece Leonardo da Vinci’s greatest masterpiece was the “Mona Lisa” which was known for its emotion & depth Leonardo’s Inventions Raphael ■ Raphael “perfected” Renaissance painting – He improved perspective and realism by studying Leonardo & Michelangelo – Raphael became the favorite painter of the Pope because of his amazing detailed paintings showing a combination of famous Greeks & Romans along with Renaissance people Raphael’s greatest painting was “School of Athens” which blended Classical figures from Greece & Rome with important people from the Renaissance Plato (drawn to look like Da Vinci) Aristotle Raphael Pythagoras Michelangelo Euclid Raphael’s “Betrothal of the Virgin” Filippo Brunelleschi ■ Brunelleschi was Florence’s greatest architect: – He studied the Roman Pantheon when he built the Cuppolo of Maria del Fiore cathedral in Florence – The dome inspired modern building designs Dome Comparisons Il Duomo, Florence US Capital, St. Paul’s, Peter’s,London Rome St. Washington, D.C. The Northern Renaissance As these ideas spread, this “Northern Renaissance” developed its own characteristics The Renaissance spread from Italy as scholars & merchants from other areas visited Italian city-states The Renaissance in France was most known for its unique architecture The Renaissance in England was most known for literature, especially the plays of William Shakespeare The Renaissance in the Netherlands was most known for realism in art Wedding Portrait by Jan Van Eyck Another important renaissance man was the inventor Johann Gutenberg’s who invention of the moveable-type printing press in 1453. He produced his first book — the Gutenberg Bible — in 1455. By 1500, presses in Europe had printed nearly 10 million books Printing made books less expensive and more available More people began to read (The Bible was a popular book) Written works became available in English, French, Spanish, Italian, or German (vernacular-the spoken language) After reading the Bible, people formed new ideas about Christianity (these ideas were different from official Church Guess if the following pieces of art (A-J) are: Renaissance or Medieval A B C D E F G H I J