* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change Impacts in the Context of Economic Globalization
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Stern Review wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Myron Ebell wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
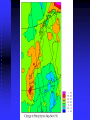
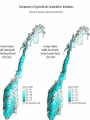
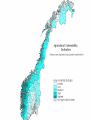
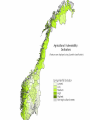
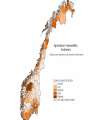
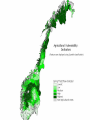
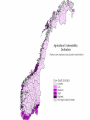
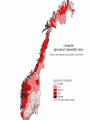
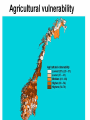
Climate Change Vulnerability in Norway Socio-economic Perspectives on Policies and Impacts Karen O’Brien CICERO Approaches to Studying Climate Change Impacts © Seppo Leinonen, www.seppo.net Impacts of Climatic Change Climatic Change Scenarios (RegClim) First-Order Impacts (Climatic Properties: temperature, precipitation) Second-Order Impacts (Crop Yields) Third-Order Impacts (Regional Productivity) Higher-Order Impacts (Farm Income, Consumer Prices, etc.) Impact Assessment Vulnerability Approaches to Impacts Vulnerability describes the extent to which a system is susceptible to sustaining damage from climate change. Aspects of Vulnerability Biophysical vulnerability Social vulnerability IPCC Conceptualization of Vulnerability Vulnerability is a function of the character, magnitude and rate of climate change and variation to which a system is exposed, its sensitivity, and its adaptive capacity. Sensitivity The degree to which a system will respond, either positively or negatively, to a change in climate. Exposure The degree of climate stress upon a particular unit of analysis Climate stress: long-term climate conditions climate variability magnitude and frequency of extreme events Adaptive Capacity The capacity of a system to adjust in response to actual or expected climate stimuli, their effects, or impacts. IPCC conclusion: ”Those with the least resources have the least capacity to adapt and are the most vulnerable.” Is Norway vulnerable to climate change? Which regions, sectors, and social groups within Norway are most vulnerable to climate change? Climate Change and Extreme Events Average annual disbursement 80-00, mill NOK, (2001value) Flooda Storma Avalanche/ landslidea Møre og Romsdal 61,7 5.4 % 91.2 % 3.2 % Hedmark 48,1 92.1 % 7.3 % 0.5 % Akershus/Oslo 46,0 53.5 % 42.8 % 3.6 % Nordland 45,0 4.2 % 87.3 % 8.5 % Hordaland 27,7 7.2 % 81.7 % 11.0 % Sør-Trøndelag 24,2 5.6 % 86.6 % 7.6 % Sogn og Fjordane 18,7 10.3 % 79.4 % 9.7 % Oppland 21,3 81.0 % 14.5 % 4.3 % Nord-Trøndelag 19,3 19.1 % 72.3 % 8.5 % Troms 22,0 5.8 % 84.8 % 8.9 % Rogaland 18,1 12.1 % 85.8 % 2.0 % Buskerud 18,0 46.6 % 33.5 % 19.8 % Telemark 15,3 46.8 % 41.7 % 11.1 % Østfold 14,1 47.7 % 48.6 % 3.6 % Finnmark 12,3 3.7 % 79.5 % 16.6 % Vestfold 10,3 19.8 % 69.1 % 10.3 % Vest-Agder 10,3 16.8 % 80.3 % 2.9 % Aust-Agder 1,7 31.7 % 60.9 % 7.2 % Fylke Vulnerable sectors: Agriculture Forestry Winter tourism Indicators of biophysical vulnerability: Agricultural sector Spring rainfall Autumn rainfall Length of growing season Spring frost/thaw Autumn frost/thaw Snow depth Indicators of social vulnerability: agricultural sector Climate sensitivity Employment in agricultural sector, % Economic capacity Untied public income (taxes and govt. transfers), NOK Employment growth prognosis, % Demographic capacity Dependency rate, % Aging working population, % Net migration rate, avg. 91-01 % How correct are these indicators? Case studies must be carried out to verify the indicators selected, and identify factors that shape vulnerability in Norwegian municipalities. Stakeholder dialogues: Voss and Oppdal (June 2003) Vulnerability is shaped by numerous social and biophysical factors Social welfare policies Globalization and regionalization Disease outbreaks Vulnerability to Climate Change Policies Sensitivity % employment in secondary sector % of CO2 emissions coming from industry Adaptive capacity Economic factors Demographic factors Vulnerability: A differential concept A dynamic concept Scale dependent Shaped by multiple stressors A vulnerability approach can improve our understanding of socioeconomic perspectives on climate impacts and policies, and help in identifying and targeting adaptation strategies. Thanks to the project team! Asbjørn Aaheim, Guro Aandahl, Sjur Kasa, Bård Romstad, Linda Sygna, Heather Tompkins, Anders Undertun (CICERO) Geir Orderud and Bjørnar Sæter (NIBR)