* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction CPX-351 Dramatically Increases Plasma Cyt and Daun
Survey
Document related concepts
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
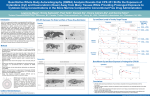
CPX-351 Markedly Reduces Renal and Hepatic Clearance Rates for Cytarabine (Cyt) and Daunorubicin (Daun) in Rats with an Associated Decrease in Excretory and Metabolic Burden Despite Providing Dramatic Increases in Systemic Drug Exposure Compared to Conventional Cyt+Daun Lawrence Mayer1, Jeffrey Fulton2, Heasook Kim-Kang2, Yijun Yi2, Peter Wang2, Paul Tardi1, Xiaowei Xie1, and Dennis Heller2 1Celator Pharmaceuticals, Vancouver, BC, Canada and Ewing, NJ, USA; 2Xenobiotic Laboratories, Inc., Plainsboro, NJ, USA CPX-351 Dramatically Increases Plasma Cyt and Daun Concentrations Introduction Cyt and Daun Excretion Much Slower for CPX-351 vs Non-Liposomal Drugs CPX-351 is a liposome formulation of Cyt and Daun in which the 5:1 molar ratio of the two drugs optimizes synergy. The marked increase in efficacy observed preclinically for CPX-351 versus the combination given in a nonliposomal (NL) saline formulation has been associated with elevated and prolonged exposure of the optimal drug ratio in bone marrow where drugloaded liposomes are preferentially taken up by leukemia cells. Clinically, CPX-351 has provided evidence of promising improvements in patient outcomes, where statistically significant increases in overall survival were observed in unfavorable/poor risk AML patient populations in two randomized Phase 2 studies. While prolonged exposure to very high drug concentrations in plasma and systemic maintenance of the 5:1 molar Cyt:Daun ratio provided by CPX-351 has scaled allometrically from rodents through to humans, little was known about its excretion and metabolic properties. Comparison of drug excretion and metabolism over time between CPX-351 and the combination NL formulation was performed in rats to better understand the pharmacodynamic relationships for CPX-351, particularly as it relates to implications for patients exhibiting reduced renal or hepatic capacity. Cytarabine Methods • Duplicate batches utilizing either [14C]Daun or [14C]Cyt were prepared for CPX-351 (5:1 molar ratio of Cyt:Daun) or saline solutions of like labeled Cyt+Daun. • Sprague-Dawley rats (4 per group) received single IV bolus doses of either 15 units/kg (15 mg/kg Cyt + 6.64 mg/kg Daun) CPX-351, or a saline solution of 300 mg/kg Cyt + 10 mg/kg Daun. These doses were selected to reflect the respective clinical doses of CPX-351 and noninfusional Cyt:Daun treatment regimens used in patients based on allometric scaling. • Radioactivity doses were 50 µCi/kg for Daun and 170-220 µCi/kg for Cyt. • Blood and plasma samples were collected and the concentrations of total [14C] determined by liquid scintillation counting. • Excreta, including bile, feces, and urine, were collected and quantified for total [14C] by liquid scintillation counting. • Pharmacokinetic parameters of the administered drug were estimated based on total [14C] content. • The profiles of parent drugs and their metabolites were determined in plasma, bile, urine and fecal samples using [14C]-radioprofiles from HPLC analyses. CPX-351 liposomes are bilamellar with a diameter of 100nm for the outer vesicle. The membrane is composed of DSPC: DSPG:Cholesterol in a 7:2:1 molar ratio. Cytarabine and daunorubicin, are encapsulated in the aqueous space of both vesicles at a 5:1 molar ratio. While inside the liposome, daunorubicin is complexed with copper, as copper gluconate, giving CPX-351 its characteristic purple color. The strength of CPX-351 is 5 units/mL where 1 unit = 1.0 mg cytarabine plus 0.44mg daunorubicin (base). The liposomes are suspended in 300 mM sucrose. Conflict of Interest Disclosure L. Mayer, P. Tardi and X. Xie are are employees of Celator Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Daunorubicin CPX-351 Exhibits Extended Circulation Half-life and Much Greater Total Drug Exposure Cytarabine Daunorubicin Cytarabine and Daunorubicin Metabolite Profiles are Similar for CPX-351 and Non-Liposomal Drugs Cytarabine and Daunorubicin Excretion Routes are Similar for CPX-351 and Non-Liposomal Drugs Conclusions Cytarabine • • • • Daunorubicin Cytarabine is eliminated via urine Daunorubicin is eliminated via bile/feces Results for CPX-351 are from intact rats with samples collected over 2 weeks Results for NL are from bile duct cannulated rats with samples collected over 72h • The profile of Cyt and Daun excretion/metabolism following CPX-351 administration is qualitatively similar to that for the NL drug combination. • The primary difference in drug elimination between these two treatments is the markedly slower rate of hepatic and urinary clearance for both drugs given as CPX-351. • The much slower drug excretion of Cyt and Daun for CPX-351 suggests that the burden on excretory and metabolic systems may be reduced for CPX-351. • Taken together, these results warrant additional clinical studies to examine whether CPX-351 provides an improved safety profile for leukemia patients with hepatic or renal insufficiencies. Abstract No. 2305, Presented at the ASH 2014 Annual Meeting: December 6-9, 2014