* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Russian Regulators: Part VI for the Nippon-Denso 770
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
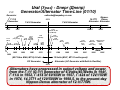
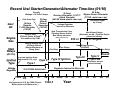
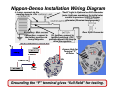
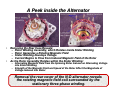
Russian Regulators: Part VI Voltage Regulator (126000-0600) for the Nippon-Denso 770-Watt Alternator Ernie Franke [email protected] 12-Volt Regulator (N-D Part # 126000-0600) for the Nippon-Denso 55-Amp Alternator • Background – Voltage Regulators Paired with Specific Generators/Alternators – Time-Line for Generators/Alternators/Regulators – Performance Specs for the Nippon-Denso (N-D) Alternator – Alternator Application in Ural Wiring • What is it? – Internal (Built-In) Voltage Regulator for the Ural Nippon-Denso (N-D) Alternator – Completely Solid-State – Years of Application: 2004-to-Present – Replaced the 14.377 (35-Amp) Alternator in Jan. 2004 – Retro-fittable to 14.377 (35-Amp) and Г-424 (11-Amp) Applications • How Does It Work? – Regulates Alternator Output Voltage to 14.5-Volts – Provides Constant Voltage Regardless of Rotor Speed – Supplies Exciter Current to Vary Magnetic Field of Rotor • Circuit Description and Operation • Replacement – Widely Used in Nippon-Denso (Denso), Daihatsu, Kubota and Suzuki Alternators – Replacement Parts Readily Purchased On-Line The Nippon-Denso 126000-0600 built-in, solid-state voltage regulator is a widely-used, reliable unit. Types of Generators/Alternators for Ural (Урал) and Dnepr (Днепр) (01/10) ( [email protected] Generator/ Alternator Type Vintage Nominal Voltage Г-11 (G(G-11) Generator DC 194119411951 6-Volt (7(7-Volt) Г-11A 11A (G(G-11A) DC 195219521957 6-Volt (7(7-Volt) 195719571974 (Built(Built-in Rectifier) Nominal Power Regulator 7-Amp 4545-Watts 7-Amp 6-Volt (7(7-Volt) 197419741998 Alternator/ Starter Alternator (Built(Built-in Rectifier & Regulator) (P/N: 72181) (P/N: 7218172181-A) Generator Г-414 (G(G-414) DC Generator (P/N: 750181) Г-424 (G(G-424) (P/N: 3701000) Hitachi (Limited Appearance) 14.3771 (P/N: 14.377114.3771010) Nippon Denso (P/N: IMZIMZ-8.10378.103718092) Current Alternator Alternator (Built(Built-in Rectifier & Regulator) Motorcycles Ural(IMZ) Dnepr (KMZ) PPPP-1 PPPP-31 (1950) M-72 Not Used 4545-Watts PPPP-31 (1950) PPPP-31A (1956) M-72, MM-72M , M-61 M-72, MM-72N, early KK-750 1010-Amp 6565-Watts PPPP-31A (1956) PPPP-302 (1963) PPPP-302A M-62, MM-63, M-66 K-650, later KK-750, K-750M, MWMW-750, MWMW-750M, MTMT-8, MTMT-9, MTMT-12 1212-Volt 1111-Amp (aka 1414-A) 150150-Watts PPPP-330 33.3702 (1992) M-67, M67.36, IMZ 8.103 Series MWMW-650, MWMW-650M, MTMT-10, MTMT-10.36, MTMT-11, MTMT-16 199819981998.5 1212-Volt (14(14-Volt) 1818-Amp 300300-Watts Internal to Alternator?? IMZ 8.103 and 8.107 “650” 650” Series Not Used 1998.5 2004 1212-Volt 3535-Amp 500500-Watts (aka 350350-W) Internal to Alternator (YA212A11E) IMZ 8.103, 8.103X, 8.123, 8.123X “650 & 750” 750” Series 20042004- 1212-Volt 5555-Amp 770770-Watts present (14(14-Volt) (14(14-Volt) (14(14-Volt) Internal to Alternator (126000126000-0600) 0600) IMZ 8.103, 8.103X, 8.123, 8.123X “750” 750” Series Not Used Not Used Notes: 1. Nomenclature: The Cyrillic letter “Г” transliterates (Russian-to-Latin) to “G” or “L” or “T.” Thus we see Г-414 or G-414 or L-414 or T-414, all for the same part. 2. Cannot use Alternator with discharged battery or without battery. Regulators are paired with specific generators/alternators. Г-11 Generator Ural (Урал) - Dnepr (Днепр) Generator/Alternator Time-Line (01/10) [email protected] Г-11A Generator 1951 Г-11A (M-72) Г-414 Generator 1957 Г-414 Г-414 (later K-750) (M-63, Г-11A Г-414 K-750M, (early K-750) (M-62) MW-750) 1955 Г-424 Alternator 1998.5 Г-424 (M-67, MT-10, MT12, MW-750) Г-11A Г-11A (KMZ M-72) (M-72N) 1950 Nippon14.3771 Denso Alternator Alternator 1974 1960 Г-424 (M-T-10.36) Г-424 (MW-650) Г-424 (M-67.36) Г-414 (M-66, MT-9) Г-414 (MT-8) 1965 1970 2004 1975 (M-72 thru M-66, MT-9) 6-Volts Г-424 (MT-16) 1980 Г-424 (IMZ 8.103, 8.107, “650”) Г-424 (MT-11) 1985 1990 1995 14.3771 Nippon-Denso (IMZ 8.103, (IMZ 8.103, 8.107, 8.123, “650 & 750”) “750”) 2000 time 2005 12-Volts (M-67, MT-10 and beyond) DC Generator Alternator (AC Generator with Built-In Rectifier) 1974 Alternators have progressed in output voltage and power, from the Г-11 (G-11) generator of 6-Volts/45-Watts in 1941, Г-11A in 1952, Г-414 of 6V/65W in 1957, Г-424 of 12V/150W in 1974, 14.3771 of 12V/500W in 1998.5, to the present-day Nippon-Denso alternator of 12-V/770W. Recent Ural Starter/Generator/Alternator Time-line (01/10) Roughly Wattage = 14 Volts X Amps 18 Amp Hitachi Starter/ Generator (300 W) Kick-Start Only 14 Amp Russian Г-424 Alternator (150 W) Gen/ Alt Engine Size Start Relays 55 Amp 35 Amp Russian Alternator: 14.3771 Nippon Denso Alternator (770 W, metal rear cap) (Hand Grenade) (500 W, black-plastic rear cap) (Increased length by 20 mm) Voltage Regulator internal to Alternator New Transmission Case (Flywheel Starter Added, New Wiring Harness) Electric-Start (E-Start) Option & Retrofit introduced by CSMI New Engine Design (Alternator on top / Flywheel Starter placed on bottom) (IMZ-8.1037-18016-12) 650 cc Factory Electric-Start (E-Start) Offered (Starter/Alternator at Timing Gear) Two Relays 750 cc Engine New Wiring Harness (9238000) One Relay One Relay (RY-115) Ignition Type Voltage Regulator No points-ignition Urals Approved for U.S. sale Type I Type II Type III Ignition ‘96 ‘97 Ural imported to U.S. by CSMI (Classic Motorcycles and Sidecars, Inc.) ‘98 Ducati (Type IV with electronics moved into airstream) Regulator Internal to Alternator 33.3720200 Solid-State 1994 ‘95 Type IV Type V ‘99 2000 ‘01 ‘02 1998.5 Year ‘03 ‘04 ‘05 ‘06 ‘07 Nippon-Denso 12-Volt Alternator (01/10) • 14-Volt / 55-Ampere / 770-Watt Alternator (actually rated at 43-Amp) • Used on; – Ural: 8.103, 8.103X, 8.123, 8.123X, “750” Series – Dnepr: Not Used (retro-fittable to Г-424 applications) • Built-In Voltage Regulator • P/N for Alternator-Only (minus cushion adaptor): 100211-1680 • Current Rating for 100211-1680 Alternator: 100211-1680 Alternator “+” Cush Adapter and Pinion Gear Engine (Crankshaft) Alternator (Rotor) Output Speed Speed Current 340-to-450 rpm 450-to-600 rpm “Fault” Light Extinguishes 30-Amp 2,025 rpm 2,700 rpm 34-Amp 2,250 rpm 3,000 rpm 3,000 rpm 4,000 rpm 40-Amp 3,750 rpm 5,000 rpm 43-Amp 5,250 rpm 7,000 rpm 46-Amp Not Much Increase above >7,000 rpm 50-Amp Motorcycle Speed (mph / kmph) Idle 22 mph / 35 kmph 24 mph / 38 kmph 32 mph / 51 kmph 40 mph / 64 kmph 56 mph / 90 kmph >56 mph / 90 kmph Nippon-Denso’s 100211-1680 alternator is nominally rated at 43-amps @ 5,000-rpm, corresponding to a motorcycle speed of 40-mph (64 km/hr). Nippon-Denso Installation Wiring Diagram L: Lamp- connect via the warning lamp to +12v “Fault” Light is Optional on N-D Alternator (note: light was mandatory for initial rotor current in previous 14.3771 35-Amp alternator (Russian hand grenade)) B+ Battery: Main current connection - connect to IG: Ignition- connect to the battery positive via ignition switched +12V, heavy duty wire. provides about 0.25-Amp to drive the regulator. Rear 2-pin Connector Access Hole for Terminal “F” of Rotor B+ Grounding the “F” terminal gives “full-field” for testing. Connections to the ND Voltage Regulator Heat Sink Regulator Case Ground Solid-state voltage regulator has only two external connections; L (output to the indicator lamp) and IG (input from the ignition switch). “L” Terminal provides ground to light the L “Fault” warning indicator. IG (Terminal P (Terminal F of Stator) of Rotor) The voltage regulator is the brain of the charging system, monitoring both battery and stator voltages. Depending on the measured voltages, the regulator will adjust the amount of rotor field current to control alternator output. ... . . . . . . . ... . . .. Inside the Nippon-Denso Voltage Regulator Alternator Rectifier Diodes 3-Ø Stator Coil Rotating Magnetic Field Rotor Coil F . E P E . B+ Protection Diodes . . B+ IG IG Ignition Switch Regulator Red “Fault” Light Sense Monolithic Integrated Circuit (MIC) . L Fuse in Fuse Block Battery L . . Grounding the “F” Terminal gives “full-field” for Testing The regulator controls the amount of battery current going to the field winding in the rotor. Ural 750 Starter / Alternator Circuit (2004-2005) ver. 2.0 (01/10) (IMZ(IMZ-8.1037170018.103717001-13, 2004 & 2005 Owners Manuals) [email protected] Notes: 1. Two Start Relays (RY-115) 2. In-Line Fuse #1 deleted mid-2005 Right Handlebar 87 RY-115 Electric Start Relay #1 (Normally Open) grn / red Momentary “Start” Button 86 “Start” 85 yel / red 30 red Rocker-Arm “Run / Kill” Switch “Kill” + . “Run” pnk/ blk Starter Motor Ignition Module 85 . (face-side) . top 1 2 1 Run Lites 2 bottom Ignition Key 3 Headlites 3 green red 4 Brakes 85 86 30 87 black white blue red (back-side) In-Line Fuse #1 red Ignition Switch 5 87 (+12V. in “Run” position) red 6 30 red gray Red (Alternator Fault) 86 white Neutral Switch (on transmission) Green (Neutral) Starter Solenoid - 9-pin Connector Headlight Cavity RY-115 Electric Start Relay #2 (Normally Open) large black + Main Output IG 55 Amp Nippon Denso Alternator L (0V.: Engine not running +12V.: Engine running and Alternator working.”) Pos + 12 Volt Battery Neg - L (lamp) IG (ignition) Notes: 1. In-Line Fuse #1 (15A) for Turn Signal and Neutral Indicator Lamp. 2. Fuse Block #4 Fuse (5A) for Ignition & Electric Start Relays. large grey Chassis Ground Connector Pin Fuse Block Male (+12V. when Ignition Switch on “Run”) black Terminal Female Ural 750 Starter / Alternator Circuit (2006-2007) ver. 2.0 (01/10) (Electrex, Inc. Rev. E, 2006 GPTT, 2006 & 2007 Owners Manuals) [email protected] Notes: 1. Single Start Relay (RY-115) 2. ND Alternator added 2004 3. In-Line Fuse #1 Deleted mid-2005 Right Handlebar Momentary “Start” Button grn/red 87 “Start” 86 yel/red RY-115 Electric Start Relay (Normally Open) red “Run” pnk/blk Headlight Cavity D E 10-pin Connector F G . + Ducati Ignition Module 85 86 30 87 16 red 18 brn/red 18 brn/red Neutral Switch (on transmission) Starter Motor 18 blu/wht 16 wht 8 red 18 brn/red + Main Output (+12V. in ”Run” position) Green (Neutral) Fuse Block 18 blk/red 15A 18 pnk/blk Ignition 14 blu Switch 1 2 3 12 Volt Battery L Neg - L (lamp) IG Chassis Ground (ignition) 18 blu Connector Pin 12 red Note: # in front of wire color is AWG wire size. Ignition Key Pos + IG 8 blk 5A 5A 12 red 18 pnk/blk 15A 14 blu 6 55 Amp Nippon Denso Alternator 18 blk/red Red (Alternator Fault) 5 Starter Solenoid 30 Rocker-Arm “Run / Kill” Switch “Kill” 18 pnk 85 Male Terminal Female Parts for NIPPON-DENSO Ural / Dnepr 12-V / 40-A Alternator Regulator Stator Connector for IG/L Rectifier Front Cover Rear Cover Brush Box with Brushes Slip Ring for Rotor Field Current Rotor Parts for the Nippon-Denso 12-Volt alternator are readily available from Tiedemann Auto-Elektric (Denmark) at www.auto-elektrik.de and Metro Auto Industrial, Pomona, CA at www.metroautoinc.com. Voltage Regulator for the Ural 100211-1680 Alternator • • • • • 12-Volt Voltage Regulator Output Voltage Set Point: 14.5-Volts Repair Circuit: VR-H2005-26S; TRI254 Terminal Markings” IG (ignition) and L (lamp) Low/High Speed RPM Charge Point (lamp on/off): 450/ 600 rpm Rotor Speed • Ambient Operating Temperature (full load): -40°C to +135°C • • • • • (-40°F to +275°F) Alternator Series: IR / IF (internal Regulator / Internal Fan) Soft-Start for Field Load Control: “Y” and Load Response: 7 sec Principal Use: Fork-lift and Industrial N-D Alternators Shut Down for: – – – – Over-Voltage Shorted “B” Lead High Field Current (over-load) Warning Light Will Illuminate The questionable 14.3771 alternator was replaced with a Nippon-Denso (N-D) alternator, adding to Ural’s reliability. Nomenclature for Nippon-Denso (N-D) Alternator • • • • • • Ural Announced: Starting January 2004, Motorcycles Equipped with DENSO 100211-1680 (Japan), with Built-In Regulator Consists of N-D 100211-680 Alternator plus Cush Adapter Unit Alternator Used In: – Line of Toyota Forklift Trucks – Ford, Kubota, New Holland Light Tractors – Thermo King AG & Industrial – Daihatsu Charadl Vehicle – Chevrolet Sprint 1.0L (1988-87) – Suzuki Samurai 1.3L (1995-86) and Sidekick 1.3L (1989) Alternator (pulley-version, instead of Ural adapter) Used In: Voltage Regulator OEM#’s: Nippon-Denso Part# 126000-0600 – Replaces: • Toyota 27700-78301 • Iseki 281-271-001-0 • Daihatsu 27700-96301, 27700-87207 • Victory A8062902 Voltage Regulator 27700-96301 Used In: – Alternators: • Ishikawajima 18504-6220 • Mitsubishi MD604589 • Nippon-Denso 100211-1550, -1670, -1680 – Vehicles: • Daihatsu • Mitsubishi • Subaru • Suzuki • Toyota Parts for the Nippon-Denso 12-Volt alternator (minus the cushion adapter) are readily available. Voltage Regulation Process • Regulator Maintains pre-Determined Charging Voltage Level: 14.5-V • When Charging Voltage Falls below this Point, Regulator Increases Field Current, thus Strengthening the Rotating Magnetic Field, Resulting in Increased Alternator Output • When Charging Voltage Rises above this Point, Regulator Decreases Field Current , thus Weakening the Magnetic Field, Resulting in Decreased Alternator Output The regulator monitors the battery voltage, controlling current flow to the rotor assembly. The rotor produces a magnetic field, which induces voltage into the stator. The rectifier bridge converts AC stator voltage to DC output for use by the motorcycle. (Compression and enhancement of Automotive Series, “Understanding the Alternator,” developed by Kevin R. Sullivan, Professor of Automotive Technology, http://www.autoshop101.com/trainmodules/alternator/alt101.html) A Peek inside the Alternator • • Removing the Rear Case Reveals: – Rotor Winding Assembly, which Rotates inside Stator Winding – Rotor Generates a Rotating Magnetic Field – Stator Winding Develops Voltage – Current Begins to Flow from Induced Magnetic Field of the Rotor As the Rotor Assembly Rotates within the Stator Winding: – Alternating Magnetic Field from the Spinning Rotor Induces an Alternating Voltage into Stator Winding – Strength of the Magnetic Field and Speed of the Rotor Affect the Magnitude of Voltage Induced into Stator Removal the rear cover of the N-D alternator reveals the rotating magnetic field coil surrounded by the stationary three-phase winding. Rotor Assembly • Basic Rotor Consists of Iron Core, Coil Winding, Two Slip-Rings, and Two, Inter-leaved, Claw-Shaped Finger Pole-Pieces • Rotor Contains Field Winding Wound over Iron Core • Surrounding the Field Coil are Two Claw-Type Finger-Poles • Each End of Rotor Field Winding Attached to a Slip-Ring • Stationary Brushes Connect Alternator to the Rotor • Magnetic Field Saturates the Iron Finger-Poles • One Finger-Pole becomes a North Pole and Other a South Pole • Rotor Spins Creating Alternating Magnetic Field; North, South, North, South, etc. The rotor (exciter) field winding creates the rotating magnetic field that induces voltage into the stator winding. Stator Windings Wye style has four stator leads. One of the leads is called the Neutral Junction, common to all the other leads. • Stator Composed of Three Sets of Windings • Each Winding Placed in Different Position Compared with the Others, Staggered 120° Apart • Laminated Iron Frame Concentrates the Magnetic Field • Stator Lead Sends Output Current to Diode Rectifier Bridge • Neutral Junction in the Wye (Y) Identified by the 6 Strands of Wire The induced AC voltage in each lead of the stator winding is fed to the diode rectifier assembly to convert to DC. Diode Rectifier Bridge Assembly • Two Rectifier Diodes Connected to each Stator Lead • Six Diodes used to rectify the AC stator voltage to DC Output Voltage • Full-Wave Rectification: Diodes Redirect both Positive and Negative Polarity AC Voltage to Produce DC Voltage The Diode Rectifier Bridge is responsible for the rectification of AC voltage to DC voltage. Slip-Rings and Carbon Brushes for Exciter Rotor Two slip rings are located on one end of the rotor assembly. Each end of the rotor field winding is attached to a slip ring, allowing current to flow through the field winding. Two stationary carbon brushes ride on the two rotating slip rings. Power for the rotor (exciter) coil is supplied, through the carbon brushes and slip-rings, by the voltage regulator.