* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exercise 7 – Differential amplifier
Survey
Document related concepts
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
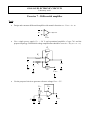
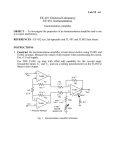
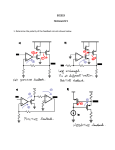
ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Laboratory work Exercise 7 – Differential amplifier Task: • Design and construct differential amplifier with transfer function uizh - UREF = Ad · ud. uizh ud UREF • Use a single power supply UCC = 20 V and operational amplifier of type 741 and the proposed topology. Differential voltage amplification should be set to Ad = 20; (ud = u2 - u1). R2 UCC R1 u1 u2 uizh R3 R4 • U REF Use the proposed circuit to generate reference voltage UREF = 5 V. UCC UCC R5 C6 R6 UREF Calculation of component value: Component values: R1 = R5 = R2 = R6 = R3 = C6 = R4 = Amplification measurements: • • • • Measure differential-mode amplification Ad = uizh / ud (ud: sine signal, U0 = 100 mV, f = 10kHz). Measure common-mode amplification As = uizh / us (us: sine signal, U0 = 1 V, f = 10kHz). While measuring Ad and As observe the alternating component of the input and output signal. Reference potential for the measurement of uizh is UREF and not GND! Obtain CMRR Differential-mode amplification: u izh ud UREF UREF Ad = uizh / ud = Ad = Ad = dB Common-mode amplification: u izh us UREF UREF As = uizh / us = As = As = dB CMRR = dB CMRR: CMRR = Ad / As = CMRR = Gain measurements of a real signal: Real excitation of the amplifier will be simulated by using a DC power source USIG, which represents a useful signal, and function generator udist, which represents common-mode disturbance (see figure below). USIG uizh UREF udist UREF Measurement 1: Set the voltage of useful signal to USIG = 20 mV. Disturbance signal udist should be represented as a sine signal with frequency of 10 kHz. Change the amplitude of the disturbance signal from 0 V to 3 V in steps of 1 V. Draw all four waveforms of the output signal to the graph. uizh / V t / µs • Increase the amplitude of the disturbance udist and find out at which value the amplifier stops working properly. What happens in the circuit at that value? Udist max = Measurement 2: Set the amplitude of sine disturbance to 2 V and frequency to 10 kHz. Change the voltage of useful signal USIG from 0 V to 60 mV in steps of 20 mV. Draw all four waveforms of the output signal to the graph. uizh / V t / µs • Increase the amplitude of the useful signal USIG and find out at which value the amplifier stops working properly. What happens in the circuit at that value? USIG max = izh – izhod, english output