* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
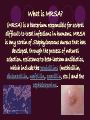
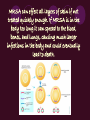
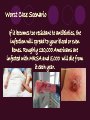
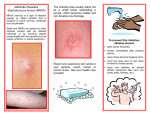
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) By: Raigan Chambers What is MRSA? (MRSA) is a bacterium responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. MRSA is any strain of Staphylococcus aureus that has developed, through the process of natural selection, resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, which include the penicillins (methicillin, dicloxacillin, nafcillin, oxacillin, etc.) and the cephalosporins. MRSA can effect all layers of skin if not treated quickly enough. If MRSA is in the body too long it can spread to the blood, bones, and lungs, causing much larger infections in the body and could eventually lead to death. Signs and Symptoms > Fever and chills > Coughing, shortness of breath > Bone pain, stiffness, or tenderness > Often painful open sores, boils, or lumps under your skin > Headache or confusion Leading Cause of MRSA Staph is a common bacteria that lives in our body. In fact, 25-30% of people already have the bacteria in their noses. Staph can become a problem if it manages to get into the body. This can happen through a cut or big wounds. Staph first appeared in Hospitals and eventually found its way to locker rooms, weight rooms, and training facilities as well. Treatment Staph can usually be treated with antibiotics but over the years, some strains, like MRSA, have become resistant to antibiotics including, methicillin, amoxicillin, penicillin, oxacillin and many others. Most doctors will drain the infection and prescribe antibiotics unless it is susceptible. They will also obtain a culture to determine how to treat the infection. Prevention of MRSA is possible by having good hygiene practices and avoiding skin contact with infected people. Also wear masks and gloves when visiting someone in the hospital and ALWAYS cover or band aid skin abrasions, cuts, burns, or any lacerations that are exposed to prevent MRSA from entering the body. Worst Case Scenario If it becomes too resistant to antibiotics, the infection will spread to your blood or even bones. Roughly 130,000 Americans are infected with MRSA and 5,000 will die from it each year. > Staph bacteria are one of the most common causes of skin infection in the U.S. >2% of the population is already colonized with MRSA > According to the CDC a estimated 10,800 deaths in the U.S. are caused by staph, 5,500 of which are linked to MRSA Works Cited http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/understanding-mrsa-methicillin-resistant-staphylococcusaureus http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/ss/slideshow-closer-look-at-mrsa http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=&imgrefurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.theguardian.com%2Fsociety%2Fmrsa& h=0&w=0&sz=1&tbnid=6B5tjrGkB8Ey9M&tbnh=174&tbnw=290&zoom=1&docid=HfuIvhQozTfIM&ei=07VSUo6UN4aWrAGm6YDIAQ&ved=0CAEQsCU http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=&imgrefurl=http%3A%2F%2Fwww2.uwrf.edu%2Fcaseit%2Fmrsa.html&h=0 &w=0&sz=1&tbnid=dSHqQO3Fd_kEXM&tbnh=175&tbnw=288&zoom=1&docid=OTcwp4QxXjrSmM&ei=eC9TUt2s DJTpqAGZ4oHYBA&ved=0CAEQsCU