* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How is Energy Stored?
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
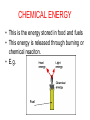
How is Energy Stored and Transferred? Emergí can be stored in a number of ways: •In chemical substances •In moving objects •In hot objects •In an object lifted up high •In a stretched or squashed object CHEMICAL ENERGY • This is the energy stored in food and fuels • This energy is released through burning or chemical reaciton. • E.g. Fuel What is the source of the chemical energy being used here? FOOD By what process is the energy released from the food? RESPIRATION In what forms is the energy being released? MOVEMENT HEAT The battery transfers stored chemical energy as electrical energy in the moving charges in the wires. When the fuel in a car reacts with the oxygeb in the air, it transfers energy to the car so that it can do useful work. KINETIC ENERGY • This is the energy that something has when it is moving. A skier will start at the top of a slope. As they move down, they faster and gain kinetic energy. THERMAL ENERGY • When a material is heated, the particles gain energy and vibrate more. • The material is gaining thermal energy and it’s temperature rises. As the particles are heated they move faster and therefore collide more. POTENTIAL ENERGY • This is the name given to the stored energy something has because of it’s position. • It is often referred to as GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY. Gravitational potential energy – stored energy which can be given out if the object falls down Energy can be changed from one form to another. TRANSFER OF ENERGY When energy is transformed from one form to another, it is not lost. We say it is CONSERVED. This is because energy cannot be made or destroyed. What happens to the energy? When energy is transferred, it ends up in a less concentrated form as it gets split up into different forms of energy: e.g. chemical energy from candle wax would be transferred into light and heat energy. As the energy is less concentrated, it is now less useful. As energy gets less and less useful, it usually ends up as low-level heating energy of the surroundings. Copy the diagram at the top of p.78 and label the energy transfers described in the text.