* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1_2_1 - Homework Market
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
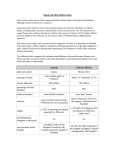
Islamic Work [Name of Student] 1. Write a brief biography of the Prophet Muhammad. Begin your account with a short discussion of how the scholar of religion’s approach to his/her subject differs from that of a member of the faith community (a Muslim). Muhammad (SAW) was born in 570CE in Mecca. His father died before his birth. His grandfather Abd al-Muttalib became his guardian. The Prophet belonged to the famous clan of Arabia called Banu Hashim. His grandfather was the respectable head of the clan. The prophet was merely six years old when he lost his mother. At the age of eight, he also lost his grandfather. After that, his uncle Abu Talib became his guardian. (Husain, 2014) Muhammad SAW grew up into a fine man with high moral values. Because of his honest nature, he was known as al-Saadiq (The Truthful One) and al-Amin (The Trustworthy One) among the people of Arab. The Prophet used to accompany his uncle in trade. A famous lady, Khadijah came to know about the Prophet and offered him to work with her. By seeing his extraordinary character, Lady Khadijah sent the proposal for marriage to the prophet which he accepted. They got married when Muhammad SAW was 25 years old. The Prophet used to spend much time in prayers and remembrance of God at a place called Ghar-e-Hira (Cave Hira). This is the place where He received revelation for the first time. After having received the message of ALLAH, he started his mission to spread the religion Islam throughout the world. He migrated from mecca to medina to spread Islam. In doing so, he faced many hardships and hurdles, but he stayed on track. Even his family members were against him and left no stone unturned to hurt him. (Authors, n.d.) Muhammad (s) was forty while, amid his one of numerous retreats to Mount Hira for reflection amid the month of Ramadan, he got the main disclosure from the Archangel Jibril (Gabriel). On this first appearance, Gabriel (as) said to Muhammad: "Iqraa," which means Read or Recite. Muhammad answered, "I can't read," as he had not got any formal training and did not know how to peruse or compose. The Angel Gabriel then grasped him until he achieved the point of confinement of his continuance and in the wake of discharging said: "Iqraa." Muhammad's answer was the same as some time recently. Gabriel rehashed the grasp for the third time, requesting that he rehash after him and said: "Recite in the name of your Lord who created! He created man from that which clings. Recite; and thy Lord is most Bountiful, He who has taught by the pen, taught man what he knew not." The mission of Prophet Muhammad (s) was to restore the love of the One True God, the maker and sustainer of the universe, as taught by Prophet Ibrahim and all Prophets of God, and to exhibit and finish the laws of good, moral, lawful, and social behavior and all different matters of importance for the mankind on the loose. In the initial three years of his main goal forty individuals (men and ladies) acknowledged Islam. This little gathering included youth and in addition more established individuals from an extensive variety of financial and social foundation. The Prophet was guided by a late disclosure to begin lecturing Islam to everybody. He then started to discuss disclosures to individuals in broad daylight and welcome them to Islam. The Quraish, pioneers of Makkah, brought his proclaiming with threatening vibe. The most threatening and nearest to the prophet was his uncle Abu Lahab and his wife. At first, they and different pioneers of Quraish attempted to pay off him with cash and power including an offer to make him ruler if he somehow managed to forsake his message. When this didn't work, they attempted to persuade his uncle Abu Talib to acknowledge the best young fellow of Makkah set up of Muhammad and to permit them to slaughter Muhammad. His uncle attempted to induce the Prophet to quit lecturing yet the Prophet said: "O uncle, if they were to put the sun in my right hand and the moon in my left hand to stop me from preaching Islam, I would never stop. I will keep preaching until Allah makes Islam prevail or I die." 2. Write a brief history of Islam from the time of the death of the Prophet in 632 C.E. until the fall of Baghdad. What were the major institutions which developed during the early centuries of Islam? After the death of the Prophet, Hazrat Abu Bakar RA received the title of the caliph. There was a clash between people that who would become the successor of Muhammad. Some people felt Hazrat Ali RA should be the successor. Under the command of Hazrat Abu Bakar Islamic power in the Arabic peninsula was gained. Abu Bakar RA died in 624 AD. After him, Hazrat Omar became the second caliph. He not only expanded the Muslim empire but also worked on the political, social, educational, judicial, military reforms of the society. He introduced many institutions for the welfare of the society. Umar RA worked on the Muslim army and used them against Syria and Palestine. Usman RA came after Omar RA as the third caliph. He ordered the revision of Quran. After Hazrat Usman, HazartAli became the fourth caliph of Islam. At that tome war started between two groups. Hazrat Ali died shortly after his succession. After two years of his death, his two sons, Hussein, and Hassan were killed. The period 786–861, particularly the caliphates of Hārūn (786–809) and al-Maʾmūn (813–833), is accounted the tallness of ʿAbbāsid standard. The eastbound introduction of the administration was exhibited by al-Manṣūr's expulsion of the funding to Baghdad in 762–763 and by the later caliphs' arrangement of wedding non-Arabs and enlisting Turks, Slavs, and other non-Arabs as royal residence protects. Under al-Maʾmūn, the scholarly and imaginative legacy of Iran (Persia) was developed, and Persian managers accepted essential posts in the Caliphate's organization. After 861, political agitation and defiance shook the realm. Tunisia and eastern Iran went under the control of inherited governors who made token affirmation of Baghdad's suzerainty. Different areas turned out to be less-solid wellsprings of income. Shīʿite and comparable gatherings, incorporating the Qarmaṭians in Syria and the Fāṭimids in North Africa, tested ʿAbbāsid standard on religious and political grounds. The Islamic armies advanced to Europe and within 100 years after the death of Muhammad the Islamic armies reached France. In the east, Muslims also flourished and reached the Pacific Ocean. The downfall of Baghdad, which lasted from January 29 until February 10, 1258, was devastating for the Muslims. The Mongols took over the capital of the Abbasid caliphate and destroyed it. References authors, w. (n.d.). Muhammad, the Messenger of God: A Brief Biographical Sketch. Retrieved from www.al-islam.org: http://www.al-islam.org/articles/muhammad-the-messenger-ofgod-a-brief-biographical-sketch-muhammad-rizvi authors, w. (n.d.). What is Islam. Retrieved from /www.truthnet.org: http://www.truthnet.org/islam/whatisislam.html Husain, A. S. (2014). Short Biography of Prophet Muhammad (s.a.w). Retrieved from www.linkedin.com: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/20140720182508-55327442-ashort-biography-of-prophet-muhammad-s-a-w