* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fill in the blanks with the correct order of the life cycle.
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
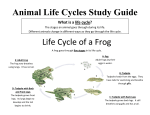
This like has a diagram of the Frog’s Life Cycle, a PowerPoint Presentation as well as activities and quizzes. http://questgarden.com/56/30/6/071017211441/process.htm This link has the plant cycle book: http://www.craftjr.com/plant-life You will need to print this book. There are two versions, one blank and one filled in. Please see below worksheets for life cycles. Facts About Life Cycles 1. A life cycle is defined as the complete succession of changes undergone by an organism during its life. A new cycle occurs when an identical set of changes is begun. 2. All organisms go through stages of development. 3. Environmental conditions such as water, temperature, and light affect the development of organisms. 4. In most mammals the stages of life go from the fertilized egg, to the fetus, the juvenile, and then to the adult. 5. Birds go from the egg, to the chick, to the adult. 6. Amphibians go from the egg, to the larva, to the adult. 7. Plants go from the seed, to the seedling , to the flowering plant. 8. Insect go from the egg, to the larva, to the pupa, to the adult. 9. Scientists can even describe the life cycle of a star or a plastic bottle. 10. Even families can have a life cycle. Most families have the parents come together as a unit. They can then have a child. The child becomes an adult. The new adult leaves home, finds a partner, produces offspring and the life cycle begins again. Plant Parts Roots Basic parts of most all plants are roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. The roots help provide support by anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients needed for growth. They can also store sugars and carbohydrates that the plant uses to carry out other functions. The roots are what carries the water and nutrients needed for plants to grow. Plant Parts - Stems Stems carry water and nutrients taken up by the roots to the leaves. Then the food produced by the leaves moves to other parts of the plant. Stems provide support for the plant allowing the leaves to reach the sunlight that they need to produce food. Where the leaves join the stem is called the node. The space between the leaves and the stem is called the internode. You'll find out why this is so important as the mystery develops. Plant Parts - Leaves Leaves are the food making factories of green plants. Leaves come in many different shapes and sizes. Leaves are made to catch light and have openings to allow water and air to come and go. The outer surface of the leaf has a waxy coating called a cuticle which protects the leaf. Veins carry water and nutrients within the leaf. Leaves are the site of the food making process called photosynthesis. In this process, carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll (the green pigment) and light energy are changed into glucose (a sugar).Photosynthesis is unique to green plants! Photosynthesis supplies food for the plant and oxygen for other forms of life. A green plant helped make the oxygen you are breathing today. Plant Parts - Flowers Flowers not only look pretty but, in fact, are important in making seeds. A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure of plants. 17. How does the leaf of a plant help the plant to survive? A) B) C) D) Leaves take nutrients from the soil. Leaves produce the food. Leaves keep the plant from falling over. Leaves take in water from the soil. 6. Which of the following would best tell you if something is a living thing? A) B) C) D) It feels soft. It is green. It produces offspring. It soaks up water. Frog Lifecycle In early spring adult frogs wake up from their long winter sleep and start making their way to breeding pools. Some frogs can travel as far as one mile to the pond which is a long distance if all you can do is hop or crawl. When the frogs reach the pond, breeding begins with the male croaking loudly to attract the female. FROG SPAWN (EGGS) When the male frog joins with the female, she releases her eggs into the water and they are fertilized by the male. The eggs or frogspawn are surrounded by jelly, which absorbs water, swells up, and floats to the surface of the pond where the sun warms it. One clump of frogspawn can contain up to 4,000 eggs. TADPOLE After about 10 days a tadpole wriggles out of each egg. At first the tadpole breathes and moves like a fish, using its gills and long tail, but after about five weeks the gills disappear and the tadpole develops lungs. The tail becomes shorter as the hind legs grow and front legs appear, lungs forms and gills disappear. It then has to swim to the surface of the water to gulp air. FROG By eight weeks the back legs have formed and by ten to eleven weeks the front legs have also appeared. At twelve to fourteen weeks the tail disappears and the tiny froglet is ready to leave the water. It will take three years before the froglet reaches maturity. When the tail is has almost disappeared it become a frog and hops out of the water. The adult frog lives on land, breathe through its lungs and eats insects. Its tail has completely disappears. Fill in the blanks with the correct order of the life cycle. Which cycle shows the correct life cycle of a frog? A) Egg - Frog - Tadpole B) Tadpole - Egg - Frog C) Egg – Tadpole - Frog D) Frog - Tadpole - Egg The complete sequence of change in a living thing is called its: A) Recycle B) Transpiration C) Life Cycle D) Spawn Life Cycle of a Butterfly A butterfly’s life has four stages -- egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Similar to other insects, butterfly begins its life as an egg. When a butterfly egg hatches, the young looks very different from the adult. It looks like a very small worm with short legs. It is called a caterpillar or larva. The larva does nothing but eat. It grows bigger and bigger until it is full size. Then it enters the third stage called the pupa. Sometimes a caterpillar spins a silk covering around itself for protection during the pupa stage. This covering is called a cocoon. When a caterpillar is in the pupa stage, a great change takes place. The worm like caterpillar turns into an adult butterfly with four large wings and six long legs. Even the mouth parts are different. The caterpillar has strong jaws for chewing leaves. But the adult has mouth parts that coil up under its head like a spring. It can extend these mouth parts into flowers to sip up the nectar. After mating, the female butterfly lays eggs and a new butterfly life cycle begins. Name ________________________________ Date:____________ Answer the following questions. Q 2: In the life cycle of a butterfly, the _____ is the primary eating and growth Q 1: Another name for 'pupa' is _________. stage of the insect. (Hint: Write the answer in lower case letters). caterpillar Answer: _______________________ adult butterfly pupa or chrysalis Q 3: What is metamorphosis? Q 4: Insects begin their life as ____. changing animals pupa changing shapes eggs staying unchanged small insects changing bodies caterpillars Q 5: The _____ is the resting or Q 6: In the ___ stage of the life cycle of a transformation stage, and within it the butterfly, the early development and marvelous transformation from caterpillar to joining of the male and female hereditary adult takes place. components take place. pupa or chrysalis egg adult butterfly caterpillar caterpillar chrysalis