* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Leakage describes an unwanted loss, or leak, of something which
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
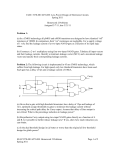
TITLE: LEAKAGE CURRENT REDUCTION IN CMOS VLSI CIRCUIT BY VECTOR CONTROL SYNOPSIS: Leakage describes an unwanted loss, or leak, of something which escapes from its proper location. In everyday usage, leakage is the gradual escape of matter through a leak-hole. Leakage current is also any current that flows when the ideal current is zero. Such is the case in electronic assemblies when they are in standby, disabled, or "sleep" mode. These devices can draw one or two microamperes while in their quiescent state compared to hundreds or thousands of milliamperes while in full operation. These leakage currents are becoming a significant factor to portable device manufacturers because of their undesirable effect on battery run time for the consumer. Referred from Microelectronic circuits by Sedra Smith, IV Edition. For reducing the leakage current of a CMOS circuit it is assumed that the system or environment produces a “Sleep” signal that can be used to indicate that the circuit is in a standby mode. There are three main sources for leakage current:(a) Source/drain junction leakage current. (b) Gate direct tunneling leakage (c) Sub-threshold leakage through the channel of an OFF transistor . The junction leakage occurs from the source or drain to the substrate through the reverse-biased diodes when a transistor is OFF. The magnitude of the diode’s leakage current depends on the area of the drain diffusion and the leakage current density, which is in turn determined by the process technology. The Gate direct tunneling leakage flows from the gate through the “leaky” oxide insulation to the substrate. Its magnitude increases 1 exponentially with the gate oxide thickness T ox and supply voltage VDD. According to the 2001 International technology Roadmap for Semiconductors, high-K gate dielectric reduced direct tunneling current is required to control this component of the leakage current for low standby power devices. And last is the Sub-threshold current, it is the drain current of an OFF transistor. This is due to the diffusion current of the minority carriers in the channel for a MOS device operating in the weak inversion mode (i.e., the sub-threshold region). For instance, in the case of an inverter with a low input voltage, the NMOS is turned OFF and the output voltage is high. Even when VGS is 0V, there is still a current flowing in the OFF NMOS transistor due to the VDD potential of the VDS. The magnitude of the sub-threshold current is a function of the temperature, supply voltage, device size, and the process parameters out of which the threshold voltage (Vth) plays a dominant role. Referred from AfshinAbdollahi, Farzan Fallah, and Massoud Pedram Journal. A detailed work is proposed to be undertaken and is planned to be carried out sequentially using different methodologies: i) ii) Leakage current of a CMOS gate is strongly dependent on the input combination applied to its inputs. The ‘sleep’ signal is used to shift in a new set of external inputs and pre-selected internal signals into the circuit with the goal of setting the logic values of all of the internal signals so as to minimize the total leakage current of the circuit. Another method which is to be implemented to reduce the leakage current is the “stack effect”. An experimental result has to be taken by using the combinational and sequential circuits. 2 iii) By using “Floating gate” methodology there is a possibility of controlling the leakage current in the CMOS circuit. A detailed study and experimental results has to be taken. Methodology : stack effect and floating gate methods Input : Giving the controlled signals with the help of matching parameters. Output : Reduction of the leakage current. Websites:en.wikipedia.org atrak.usc.edu/~massoud/Papers/leakage-control-journal.pdf cadlab.ece.ucsb.edu *** 3