* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Filter Circuits
Survey
Document related concepts
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ringing artifacts wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Analogue filter wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
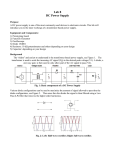
Block diagram of a Power Supply Filter Circuits • The output from the rectifier section is a pulsating DC. • The filter circuit reduces the peak-to-peak pulses to a small ripple voltage. • The conversion of ac to dc by a rectifier by including a filter between the rectifier and the load resistance to reduce the ripple components of the output voltage. 2 Types of Filter Circuits • Series Inductor Filter • Shunt Capacitor Filter • LC (or) L-Section Filter, and • CLC (or) ∏-Section Filter 3 Shunt Capacitor Filter Shunt Capacitor Filter Shunt Capacitor Filter • The instant at which the diode gets forward biased, the capacitor instantaneously acts as short circuit and a surge current flow through a diode. • When the diode is non-conducting, the capacitor discharges through load resistance RL. • Total amount of charge that flows through conducting diode (or) diodes to recharge the capacitor must be equal to the amount of charge lost during the period when the diode (or) diodes are non-conducting and capacitor is discharging through load resistance RL.