* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are examples of common agonists and antogonists?
Survey
Document related concepts
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
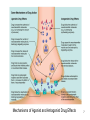
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
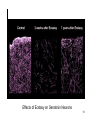
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
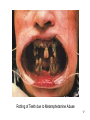
Serotonin syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Psychology 304: Brain and Behaviour Lecture 15 1 Neuropharmacology 1. What neurotransmitters have been identified? (continued) 2. How do drugs affect the conduction and transmission of electrochemical neural signals? 3. What are examples of common agonists and antogonists? 2 What neurotransmitters have been identified? (continued) • Large-molecule neurotransmitters are neuropeptides: Found largely in neurons of the CNS. Include five categories: pituitary peptides, hypothalamic peptides, brain-gut peptides, opioid peptides, and miscellaneous peptides. 3 The function of each neuropeptide depends upon its amino acid sequence. Associated with analgesia, reinforcement, feeding, learning, and memory. 4 How do drugs affect the conduction and transmission of electrochemical neural signals? • Drugs: Exogenous chemicals that are not necessary for normal functioning and significantly alter cellular functioning when taken in relatively low doses. • May be introduced into the central nervous system through diverse means. 5 • Drugs may be classified as agonists or antagonists. • Agonists facilitate the effects of neurotransmitters. Antagonists inhibit the effects of neurotransmitters. • Agonists and antagonists may influence synaptic transmission in a number of ways: 6 Mechanisms of Agonist and Antagonist Drug Effects 7 What are examples of common agonists and antogonists? • Examples of common drugs that act as agonists are: L-DOPA: Serves as a precursor for dopamine. Alcohol: Stimulates the release of dopamine; stimulates postsynaptic receptors for GABA. Cannabis: Stimulates the release of dopamine. 8 Phencyclidine (PCP): Stimulates the release of dopamine. Ecstasy (MDMA): Stimulates release of serotonin. Caffeine: Blocks autoreceptors for dopamine. Nicotine: Stimulates postsynaptic receptors for acetylcholine. 9 Effects of Ecstasy on Serotonin Neurons 10 Non-Users of Ecstasy Users of Ecstasy Effects of Ecstasy: Non-Users vs Users. 11 Tranquilizers (i.e., benzodiazepines; e.g., Valium): Stimulate postsynaptic receptors for GABA. Tricyclic antidepressants: Block reuptake of serotonin and norephinephrine. SSRI antidepressants: Block reuptake of serotonin. St. John’s Wort: Blocks reuptake of serotonin; inhibits enzymes that break down monoamines (e.g., serotonin). 12 Cocaine: Blocks reuptake of dopamine. Amphetamine: Stimulates release of dopamine and norephinephrine, blocks the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine. 13 Coca-Cola Ads 14 Coca Wine Ad 15 Ad for Cocaine-Based Toothache Drops 16 Rotting of Teeth due to Metamphetamine Abuse 17 Physical Impact of Metamphetamine Abuse 18 Neuropharmacology 1. What neurotransmitters have been identified? (continued) 2. How do drugs affect the conduction and transmission of electrochemical neural signals? 3. What are examples of common agonists and antogonists? 19