* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (Blood Typing).
Survey
Document related concepts
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
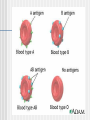
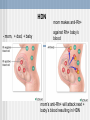
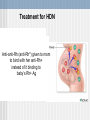
CV system Ch 10 Blood and Genetics PPT 2 Genetics Vocabulary Gene- inherited unit, determines traits Allele- copy of gene Dominant- allele, capital letter, “A” Recessive- allele, lower case letter, “a” Genetics Homozygous- 2 same alleles, “AA” “aa” Heterozygous- 2 diff. alleles, “Aa” Genotype- alleles “AA” “Aa” “aa” Phenotype- physical expression of genotype Punnett square- tool to figure out probability of possible offspring Human ABo Blood Typing RBC’s contain proteins called antigens (agglutinogens)(Ag) on their surface Blood type is determined by which Antigen is present on the surface of the RBC 2 Ag’s = A , B Human ABo Blood Typing Blood types have proteins called antibodies (agglutinins) (Ab’s) in the plasma opposite of antigens present 2 Ab’s = anti-A , anti-B Human ABo Blood Typing Codominance- two alleles equally dominant Multiple alleles- more than 2 alleles for a gene or trait 3 alleles IA IB both dominant i (recessive for type O) Human ABo Blood Groups Blood type(phenotype) genotypes ______________________________ A IAIA, IAi B IBIB, IBi AB IAIB O ii Blood types Ag’s present Ab’s present (phenotype)__________________________________ A A anti-B B B anti-A AB A and B none O None anti-A and anti-B Ex blood typing problem Heterozygous A woman and homozygous B man have children, what are genotypes and phenotypes of children? Parents IAi IBIB Offspring G: 1/2 IAIB and 1/2 IBi P: 1/2 type AB blood, 1/2 type B blood Blood Transfusions Universal donor- Type O, no Ag’s, both Ab’s (no antigens for other blood types to recognize (”its invisible to other blood types) Universal recipient- Type AB, no Ab’s, both Ag’s (no antibodies to recognize other blood types introduced) Transfusion- transfer of organ or blood from donor to recipient Blood transfusions Ab’s(antibodies) agglutinate with Ag’s (antigens) if wrong blood type given in a transfusion Transfusion reaction (bad) = agglutination Hemolysis of RBC’s Hemolysis: destruction of RBCs Rh Blood Typing Another Ag on surface of RBC = Rh+ Ab (antibodies against it) can be made if negative blood (Rh -) is exposed to/mixed with Rh+ antigen. The Antibody is called anti-Rh+ 2 alleles Rh+ dominant Rh- recessive Rhesus monkey Rh Blood typing Phenotypes genotypes _______________________________ + blood Rh+Rh+ Rh+Rh-blood Rh-Rh- Rh Blood Typing Blood type Ag present Ab ______________________________ + Rh+ none - none can make anti-Rh+ Hemolytic disease of the newborn Rh Blood Typing and HDN If Rh- blood mixed with Rh+ blood, then person with Rh- blood makes anti-Rh+ against Rh+ blood!...leads to agglutination When can this occur? Transfusions and pregnancy HDN - mom, + dad, + baby mom makes anti-Rh+ against Rh+ baby’s blood mom’s anti-Rh+ will attack next + baby’s blood resulting in HDN Treatment for HDN Anti-anti-Rh (anti-Rho) given to mom to bind with her anti-Rh+ instead of it binding to baby’s Rh+ Ag Ex Rh factor problem Heterozygous + woman and - man have children, what are genotypes and phenotypes of children? Parents Rh+Rh- Rh-Rh- Offspring G: 1/2 Rh+Rh-, 1/2 Rh-RhP: 1/2 + blood, 1/2 - blood Review…so far… Blood Types? Universal Donor? Universal Recipient? What is agglutination? Why does it occur? Genotypes for Rh +, Rh -? What is HDN? Why does it occur? Blood Dihybrid Problem ABo and Rh factor Two traits (Abo AND Rh factor) Need to FOIL Blood Dihybrid Problem ABo and Rh factor Homozygous type A, - blood man Type AB and heterozygous + woman Parents: (man) IAIARh-Rh- (woman) IAIBRh+Rh- FOIL…… (man) IARh- IARh- IARh- (woman) IARh+ IARh- IBRh+ IARhIBRh- Dihybrid Problem continued Offspring G: 4 IAIARh+Rh4 IAIARh-Rh4 IAIBRh+Rh4 IAIBRh-RhP: 4 A+ 4A- 4AB+ 4 AB- Sex determination 2 Sex chromosomes : Genotypes of: X (male) XY Y (female) XX Sex linkage Sex linked trait- recessive trait linked to X chromosome (ex. hemophilia) Ex. hemophilia ___= normal clotting,____= hemophilia (on X chromosomes only) Carrier- carries disease but doesn’t express it, usually females Alleles: XH Xh Y Sex linked hemophilia Phenotype genotype _______________________________ Female, normal XHXH Female, normal but “carrier” XHXh Female, hemophiliac XhXh Male, normal X HY Male, hemophiliac XhY Sex linked hemophilia problem Normal clotting woman and normal clotting male have children some of whom have hemophilia and some of whom are normal, what are genotypes of parents? Genotypes of parents: XHXh and XHY Proof: children XHXH, XHY, XHXh- all normal XhY- hemophiliac