* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Progress with Assessment of Data-Limited Stocks
Survey
Document related concepts
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Conservation movement wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Operation Wallacea wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Marine conservation wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
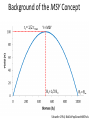
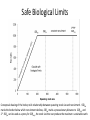
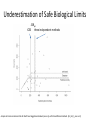
Legal Governance of European Fisheries Rainer Froese Law of the Sea in the 21st Century CAU, Kiel, 8.03.2014 Overview • • • • • The MSY concept Safe biological limits Status of European fish stocks UNCLOS and the Common Fisheries Policy Conclusions MSY, Bmsy and Fmsy • • • • MSY is the maximum sustainable yield Biomass (B) is the weight of the fish in the sea Bmsy is the biomass that can produce MSY Fmsy is the fishing pressure that eventually results in Bmsy and MSY • A stock is and remains in good status if B > Bmsy and F < Fmsy Background of the MSY Concept Schaefer 1954; BioDivPopGrowthMSY.xls Surplus Production Implications • Surplus production (Y) is the production of biomass beyond what is needed to maintain current population size • If a fishery only catches the surplus production, then the population size remains • If a fishery catches more, then the population shrinks • If it catches less, then the population grows Surplus Production Implications • Surplus production has a maximum at about half of unexploited population size B∞ • Keeping a population at 0.5 B∞ allows catching MSY forever • A population is kept stable if the fishing rate F equals the intrinsic growth rate rt • MSY is reached at ½ B∞ and ½ rmax • Thus, MSY is reached at Fmsy = ½ rmax The Past Common Fisheries Policy (until 2013) • Apply a precautionary approach to fishing • Keep fish stocks within safe biological limits Safe Biological Limits Conceptual drawing of the hockey stick relationship between spawning stock size and recruitment. SSBlim marks the border below which recruitment declines, SSBpa marks a precautionary distance to SSBlim, and 2 * SSBpa can be used as a proxy for SSBmsy, the stock size that can produce the maximum sustainable catch. Current Status of European Stocks Communication of the Commission in 2013: “The number of overfished stocks (where the most recent fishing mortality is higher than that which will provide MSY) has fallen from 47% last year to 39% this year.” Brussels, 30.5.2013, COM(2013) 319 final Status of European Stocks Extending the trends in the last 3 years for the 95% confidence limits… SSBpa UNCLOS UNFSA Based on the ICES Stock Summary database 10/2013 with data for 45 stocks [relF_relB.xlsx] Scientific Advice • Management decisions are to be “based on best available scientific advice” • But how independent and good is that advice? Independence of Scientific Advice • Most fisheries scientist in Europe are directly or indirectly employed by the Ministers of Agriculture (the same who decide about fisheries management in Brussels) • ICES (the advisory body to the EC) is an intergovernmental organization. The policysetting Council of ICES consists of national representatives who are determined by the Ministers of Agriculture (the same…) Quality of Scientific Advice • Fisheries science holds that mortality caused by sustainable fishing (Fmsy) should be less than natural mortality (M) caused by e.g. predation, diseases, natural hazards or old age • Doubling mortality reduces life time and reproductive phase by half and also reduces average size and fecundity • However, in 29 of 38 stocks (76%) with available data, the ICES estimate of Fmsy exceeded M, on average by 62% Fishing Mortality may be Higher True F/Fmsy may be higher because of unrealistically high Fmsy in 76% of the stocks Based on the ICES Stock Summary database 10/2013 with data for 45 stocks Quality of Scientific Advice • ICES provides estimates of the border of safe biological limits (SSBpa). Below SSBpa recruitment may be reduced and the stock is at increased risk of collapse • In 14 of 43 stocks (33%) with available data, the ICES estimate of SSBpa fell below the median estimate of three independent scientific methods. Underestimation of Safe Biological Limits SSBpa ICES three independent methods Analysis of stock-recruitment data for North Sea Doggerbank Sandeel (san-ns1), with three different methods. [S-R_HS_5_san-ns1.r] Stock Biomass may be Lower True SSB/SSBpa may be lower because of unrealistically low SSBpa in 33% of the stocks Based on the ICES Stock Summary database 10/2013 with data for 45 stocks UNCLOS & UNFSA in the CFP Article 2.2 • The CFP shall apply the precautionary approach to fisheries management, and shall aim to ensure that exploitation of living marine biological resources restores and maintains populations of harvested species above levels which can produce the maximum sustainable yield. • In order to reach the objective of progressively restoring and maintaining populations of fish stocks above biomass levels capable of producing maximum sustainable yield, the maximum sustainable yield exploitation rate shall be achieved by 2015 where possible and, on a progressive, incremental basis at the latest by 2020 for all stocks. CFP beyond UNCLOS Preamble of CFP Whereas: ... • (11) The CFP should contribute to the protection of the marine environment, to the sustainable management of all commercially exploited species, and in particular to the achievement of good environmental status by 2020, as set out in Article 1(1) of Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council1. • (13) An ecosystem-based approach to fisheries management needs to be implemented, environmental impacts of fishing activities should be limited and unwanted catches should be avoided and reduced as far as possible. • (16) The CFP should pay full regard, where relevant, to animal health, animal welfare, food and feed safety. CFP beyond UNCLOS Preamble of CFP • (22) In order to contribute to the conservation of living aquatic resources and marine ecosystems, the Union should endeavour to protect areas that are biologically sensitive, by designating them as protected areas. In such areas, it should be possible to restrict or to prohibit fishing activities. When deciding which areas to designate, particular attention should be paid to those in which there is clear evidence of heavy concentrations of fish below minimum conservation reference size and of spawning grounds, and to areas which are deemed to be biogeographically sensitive. Account should also be taken of existing conservation areas. [....] CFP beyond UNCLOS • Article 2.3 The CFP shall implement the ecosystem-based approach to fisheries management so as to ensure that negative impacts of fishing activities on the marine ecosystem are minimised, and shall endeavour to ensure that aquaculture and fisheries activities avoid the degradation of the marine environment. Precautionary Principle in CFP • Article 4.1 (8) 'precautionary approach to fisheries management', as referred to in Article 6 of the UN Fish Stocks Agreement, means an approach according to which the absence of adequate scientific information should not justify postponing or failing to take management measures to conserve target species, associated or dependent species and non-target species and their environment; • [But no mentioning that, in case of uncertainty, the option that will lead to less potential damage has to be chosen] CFP beyond UNCLOS • Article 4.1 (9) 'ecosystem-based approach to fisheries management' means an integrated approach to managing fisheries within ecologically meaningful boundaries which seeks to manage the use of natural resources, taking account of fishing and other human activities, while preserving both the biological wealth and the biological processes necessary to safeguard the composition, structure and functioning of the habitats of the ecosystem affected, by taking into account the knowledge and uncertainties regarding biotic, abiotic and human components of ecosystems; Article 4.1 (11) 'low impact fishing' means utilising selective fishing techniques which have a low detrimental impact on marine ecosystems or which may result in low fuel emissions, or both; CFP beyond UNCLOS • Article 4.1 (17) 'minimum conservation reference size' means the size of a living marine aquatic species taking into account maturity, as established by Union law, below which restrictions or incentives apply that aim to avoid capture through fishing activity; such size replaces, where relevant, the minimum landing size; CFP beyond UNCLOS Article 8, Establishment of fish stock recovery areas 1. The Union shall, while taking due account of existing conservation areas, endeavour to establish protected areas due to their biological sensitivity, including areas where there is clear evidence of heavy concentrations of fish below minimum conservation reference size and of spawning grounds. In such areas fishing activities may be restricted or prohibited in order to contribute to the conservation of living aquatic resources and marine ecosystems. Conclusion • After New Zealand, Australia and USA, the EU has finally written into regional law the “fishing” norms of the Law of the Sea • Implementation and enforcement will have to follow next • Independence of scientific advice has to be ensured and quality has to be verified (need for a formal way to challenge ‘wrong’ advice) Thank You