* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geocentric vs. Heliocentric
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Patronage in astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
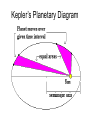
Geocentric vs. Heliocentric A Battle for the Ages The Beginnings of the Geocentric Model of the Universe Early Greek Astronomy • Aristotle (384 – 322 BCE): States that the Universe is a perfect sphere with Earth at the center. • Objects in space also move in perfect circles. Early Greek Astronomy • Ptolomy (140 AD): Still believed that Earth was center of Universe (geocentric theory). Noticed that Aristotle’s model did not explain planetary movements. • Planets and stars moved in EPICYCLES. In other words planets move in perfect CIRCLES WITHIN CIRCLES! Ptolemaic System Mars Jupiter Ptolemy’s system provided the intellectual framework for all discussion of the universe for nearly 1600 years!! So in a very true sense, this idea was stupendously successful even though we now know that it was incorrect. Saturn Earth & Moon Mercury Sun Venus The Revolution of Ideas The Beginnings of the Heliocentric Model of the Universe Copernicus (1473-1543) A Polish Astronomer The Copernican Revolution! Copernicus 1. Earth is not the center of “everything.” 2. All the planets revolve around the Sun! (heliocentric theory) 3. Stars are very much farther away than the Sun 4. Any motion of the stars is a result of the Earth’s rotation 5. Still used “perfect” circles for the orbits. Changing Ideas is Not Easy. Copernicus was no fool. He waited until his own death before he published his new ideas. On March 5, 1616, Copernicus' work was banned from being taught and discussed by the Congregation of the Index "until corrected." It stayed on this list of prohibited books and teachings until 1822!!!! Italian scientist • Galileo Galilei 1600s): (late 1500s - early First to point the refracting TELESCOPE towards the heavens. He studied the movement and orbits of many nearby planets in our solar system. • Offered PROOF to Copernicus’s Heliocentric Model of our Universe. • Led to the discovery of the moons of Jupiter Galileo Galilei The Great Compromise Tycho Brahe (1546-1601) Danish Nobleman Experimentalist & Observer. Made very careful measurements of star’s positions. Earth must be stationary. Tychonic Model Tycho developed a system that combined the best of both worlds. He kept the Earth in the center of the universe, so that he could retain Aristotelian physics and Ptolemy’s geocentric idea. The Moon and Sun revolved about the Earth, and the shell of the fixed stars was centered on the Earth. But Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn revolved about the Sun. Tychonic Model The German Student • Johannes Kepler (early 1600’s): Followed Tycho’s work BUT followed the Heliocentric Model. • Used Math to calculate that planets moved in ORBITS and along ELLIPSES. Newton’s Idea of Law of Universal Gravitation Supported Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion Kepler’s Planetary Diagram Issac Newton •English scientist (mid 1660’s) •3 laws of motion explain how the inertia of a planet with gravity causes orbital motion. •Also, developed the reflecting telescope. Today!