* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ROOTS AND STEMS
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
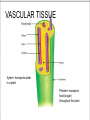
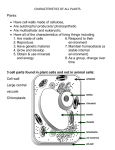
ROOTS AND STEMS What is their role in photosynthesis? Functions of Roots The primary functions of roots are: 1) to anchor the plant (tap root vs. fibrous root) 2) to absorb water and minerals (root hairs can penetrate spaces between soil particles) 3) to store nutrients (ex. carrots and sweet potatoes store carbohydrates) ROOTS What is the difference between primary roots and secondary roots? Primary roots are the initial roots that grow from a seed. Secondary roots branch out from the primary root Tap root vs. Fibrous root the primary root grows longer and thicker than the secondary roots the secondary roots continue to grow, and eventually all the roots are of equal or nearly equal size How do these root parts help with photosynthesis? Functions of Stems The primary function of stems is to: 1) transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves and, at the same time, to transport food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. 2) Stems may also function as food storage areas, supporting structures, and places for the growth of new plants. Vascular Tissue in Stems Monocot Dicot (named for how many seed leaves are present in an embryo plant-ONE) (named because the embryo within Vascular bundles are scattered throughout a dicot seed contains TWO leaves) Vascular bundles are found in a circular pattern Vascular tissue contains the xylem and the phloem The xylem and the phloem have the same function in the stem as they do in the leaf – what is their function? VASCULAR TISSUE Xylem= transports water in a plant Phloem= transports food (sugar) throughout the plant Woody Stems vs. Herbaceous Stems Woody stems are hard and often turn brown yet they grow bigger year after year. Herbaceous stems are soft and remain green for the life of the plant. How do these stem parts help with photosynthesis? Tree Rings What do they tell us?