* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam - WordPress.com
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
History of slavery in the Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Islamic views on slavery wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
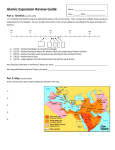
All of the following are characteristics of Islam except: A. a monotheistic belief in one god that must be worshipped as one god. B. a belief in a community of believers unified by their faith above all else C. a tradition of passing down the central teachings of their faith orally D. a spreading of the faith to the 3 continents of Europe, Asia and Africa E. a belief in the importance of prayer, fasting, and charity. The Caliph A. always ruled over one extended area of land from Spain to India B. was a position that dissolved a short time after Muhammad’s death C. was a position passed down through one family that traced its roots though Mecca D. was a position created by the Abbasid family to solidify their rule in Baghdad E. was considered to be the successor of Muhammad as well as their political leader The Muslim caliphate is significant in world history because A. it is the first Afro-Eurasian empire B. it peacefully incorporated many different cultural groups C. it became the largest empire in history D. it is significantly improved the living standards of all its subjects E. its beginnings as a nomadic culture made it remarkably egalitarian in its dealing with genders Islamic Sects During the Umayyad Dynasty, the Umma split over the issue of leadership Shi’ites = resisted Umayyad rule Believed the caliph should be a descendent of Muhammad Sunnis = accepted Umayyad rule Believed the caliph should simply follow Muhammad’s actions Law and Dogma During the time of Muhammad, Islam had no legal system Followers simply followed the Five Pillars and Muhammad’s personal examples (sunna) After Muhammad’s death, an ethical code based on his actions (the hadith) was created Sharia = the law code (legal system) that developed from these actions Served as the foundation for Islamic civilizations Converts and Cities Conversion was simple and common throughout Islamic Empires At first, conversion occurred due to military expansion Later, the religion spread as a result of missionaries and merchants Because there is no established priesthood, converts usually moved to urban centers (ex. Baghdad) to be around Muslims Learned Arabic, visited Mosques, etc… Gender Roles in Islam Patriarchal Role of men Could be polygamous Educated Feared sexual infidelity and meddling in politics by women Role of women Covered themselves in public and lived in relative seclusion Few became literate Could remarry, initiate divorce, inherit property “Say to the believing men that they should lower their gaze and guard their modesty; that will make for greater purity for them; and Allah is well acquainted with all that they do. And say to the believing women that they should lower their gaze and guard their modesty; and that they should not display their beauty and ornaments except what must ordinarily appear thereof; that they should draw their veils over their bosoms and not display their beauty except to their husbands…” Slaves in the Muslim World Islam allowed slavery, but forbade enslaving other Muslims or “People of the Book” Not hereditary Many slaves gained freedom by converting to Islam Most slaves came from East Africa and were traded throughout the Indian Ocean into Asia (Islamic Slave Trade)