* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes 4.3
Survey
Document related concepts
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
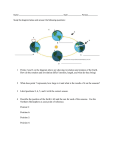
Notes Chapter 4 Earth’s Structure and Motions Name __ _____ 4.3 Earth’s Revolution pgs. 80 – 83 1. Earth’s revolution _______________________ – one complete orbit around the sun = 1 year – ____________ days – Leap year? _________________________________________________ ___________________- tilt of axis is parallel throughout our orbit (N. Star) 2. Length of daylight Depends on two things: – ___________ ____ ____________ – _________________ in orbit – causes seasons 3. Proof of revolution __________________ – apparent shift in position of nearby stars. 4. Path and rate of revolution Earth’s orbit is _________________ Average distance _______________ miles (150 million km) _________________ – point in earth’s orbit when farthest from the sun (______________ ) ___________________ – point in earth’s orbit when nearest to sun (________________) 5. Effects of revolution and tilt _______________ _______________ of daylight Indirect and direct rays 6. Seasons Solstices – _______________ – June 21, direct rays on T. of Cancer, _____________ day – Winter – December 21, direct rays on T. of ___________________, shortest day Equinox equal day and night sun rises due ______ and sets due ______ – ____________________ – march 21 vertical rays at equator. 12 hrs. Day and 12 hrs. night. – ____________________ – Sept 23 vertical rays at equator. 12 hrs. Day and 12 hrs. night – Label the diagram below with the seasons, date and vertical rays Our axis has not always pointed to the same star and will change in the near future. ___________________– earth not only rotates on its axis … it also wobbles. This wobble effect is a phenomenon caused by forces exerted by the sun on the bulges of the earth at the equator