* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the heart <3
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
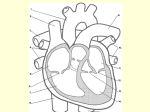
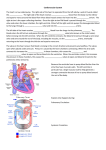
THE HEART <3 BLOOD AND THE HEART FUN FACTS ♦ An average adult human contains about 5 liters (5.3qt) of blood. ♦ The blood makes up about onethirteenth of the body’s weight. ♦ The adult heart weighs about 280 grams (10 oz.) ♦ At rest, the heart pumps out about 80 millimeters (2.6 oz) of blood with each beat. ♦ The heart beats, on average, 70 times each minute at rest. ♦ This means all the blood is circulated (goes round the body once) in about one minute. ♦ During strenuous exercise the heart can pump six to eight times the amount of blood that it pumps at rest. Superior vena cava and inferior vena cava – bring deoxygenated blood to right atrium Pulmonary artery – takes blood away from right ventricle to the lungs for O2 Pulmonary veins – bring oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium Aorta – takes blood away from left ventricle to rest of the body Chambers and Valves • SEPTUM divides into R and L halves • Upper chambers – RIGHT ATRIUM and LEFT ATRIUM • Lower chambers – RIGHT VENTRICLE and LEFT VENTRICLE • Four heart valves permit flow of blood in one direction -TRICUSPID VALVE – between right atrium and right ventricle -BICUSPID (MITRAL) VALVE – between left atrium and left ventricle -Semilunar valves are located where blood leaves the heart - PULMONARY SEMILUNAR VALVE and AORTIC SEMILUNAR VALVE The heart=a muscular double pump with 2 functions The right side receives oxygen-poor blood from the body and tissues and then pumps it to the lungs to pick up oxygen and dispel carbon dioxide Its left side receives oxygenated blood returning from the lungs and pumps this blood throughout the body to supply oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues 8 9 Two circulations Systemic circuit: blood vessels that transport blood to and from all the body tissues Pulmonary circuit: blood vessels that carry blood to and from the lungs Chambers of the heart sides are labeled in reference to the patient facing you Two atria Right Left atrium atrium -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Two ventricles Right Left ventricle ventricle 10 Valves three: tricuspid one: bicuspid to pulmonary trunk (branches R and L) Bicuspid valve (the bicuspid one) LA to RV Pulmonary valve RV (cusp means flap) “Tricuspid” valve RA 11 to LV Aortic valve LV to aorta Function of AV valves 12 Function of semilunar valves (Aortic and pulmonic valves) 13 Meet the Heart http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vi1JK6IYVt8 Pattern of flow 15 (simple to more detailed) Body RA RV Lungs LA LV Boby Body to right heart to lungs to left heart to body Body, then via vena cavas and coronary sinus to RA, to RV, then to lungs via pulmonary arteries, then to LA via pulmonary veins, to LV, then to body via aorta From body via SVC, IVC & coronary sinus to RA; then to RV through tricuspid valve; to lungs through pulmonic valve and via pulmonary arteries; to LA via pulmonary veins; to LV through mitral valve; to body via aortic valve then aorta LEARN THIS PHYSIOLOGY OF THE HEART The heart is a double pump. When the heart beats… Right Heart Deoxygenated blood flows into heart from vena Cava ---right atrium ---tricuspid valve--right ventricle --pulmonary semilunar valve--pulmonary artery ---lungs (for oxygen) Left Heart Oxygenated blood flows from lungs via pulmonary Veins--- left atrium--- mitral valve--- left ventricle--aortic semilunar valve--- aorta --- general circulation (to deliver oxygen) Control of Heart Contractions SA (sinoatrial) NODE = PACEMAKER • Located in right atrium • SA node sends out electrical impulse • Impulse spreads over atria, making them contract • Travels to AV Node AV (atrioventricular) NODE • Conducting cell group between atria and ventricle • Carries impulse to bundle of His BUNDLE OF HIS • Conducting fibers in septum • Divides into R and L branches to network of branches in ventricles (Purkinje fibers) PURKINJE FIBERS • Impulse shoots along Purkinje fibers causing ventricles to contract Flow Through the Heart http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7XaftdE_h60 Heart Contraction SA Node Sinalarterial node “Pacemaker” AV Node Atrioventricular node Allows impulse to cross into ventricles Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje Fibers Heart Contraction Flow Chart SA Node fires ↓ Impulse spreads across atria ↓ Atria depolarizes ↓ Atria contract (lub) ↓ Blood is pumped to the ventricles ↓ AV Node receives impulse from SA Node ↓ Impulse passes through bundle of His ↓ Impulse passes through Purkinje fibers ↓ Ventricles depolarize and contract (dub) ↓ Blood is pumped into the lungs and out to the body Electrical conduction system: 21 specialized cardiac muscle cells that carry impulses throughout the heart musculature, signaling the chambers to contract in the proper sequence (Explanation in next slides) Conduction system SA node (sinoatrial) In wall of RA Sets basic rate: 70-80 Is the normal pacemaker Impulse from SA to atria Impulse also to AV node via internodal pathway AV node In interatrial septum 22 Conduction continued SA node through AV bundle (bundle of His) Into interventricular septum Divides R and L bundle branches become subendocardial branches (“Purkinje fibers”) Contraction begins at apex 23 24 EKG→ measures heart electricity P Wave→ Atria contract & Depolarize PQ Interval→ Impulse is passing through the bundle of His to the Purkinje fibers QRS Wave→ Ventricles depolarize and contract T Wave→ Ventricles repolarize Cardiac Cycle Blood enters the atria through the vena cava (R) and the Pulmonary vein (L) ↓ Atria will contract ↓ Blood is pushed through the AV valves into the ventricles ↓ Ventricles contract and AV valves close ↓ Blood is pushed though the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves into the pulmonary trunk and the aorta ↓ Ventricles relax and valves close Cardiac Cycle Tutorial http://faculty.alverno.edu/bowneps/cardiaccycle/cardiaccycle1m ap.htm