* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune - lymphatic system
Survey
Document related concepts
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
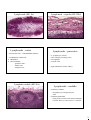
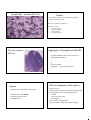
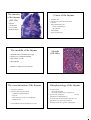
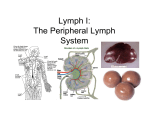
Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system ♣ organised lymphoid structures ♣ cell components - histology & embryology ← lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles ← accessory cells ♦monocytes-macrophages system♦ Immune defense: Immune response: INNATE IMMUNITY - surface protective system - blood proteins: complement system - phagocytic cells, NK cells ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY - humoral - cell-mediated • The ability to distinguish „self“ a „nonself“ → immune defence x immunodeficiency → autotolerance x autoimmune diseases → immune supervision x hypersensitivity Lymphoid organs Primary: • bone marrow • thymus Secondary: • spleen (lien) • lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici) • tonsils • diffuse lymphatic tissue in the mucosa of some systems (GALT, BALT) Structure of a lymph node • convex face - „afferent“ • concave hilum - „efferent“ • • • • capsule => trabecule outer cortex inner cortex (paracortical layer) medulla 1 Lymph node (HE 8x) Lymph node - capsule (HE 128x) Lymph node - cortex • subcapsular sinus → intermediate sinuses • LYMPHATIC NODULE: ℵ PRIMARY ℵ SECUNDARY: - germinal centre - mantle zone - marginal zone Lymphatic nodule (HE 50x) Lymph node - paracortex • • • • T- lymphocytes (CD4+) APC (antigen presenting cells) macrophages reticular cells • high endothelial venules (HEVs) Lymph node - medulla • medullary CORDS – B-lymphocytes and plasmocytes – APC • medullary SINUSES – lining of the reticular cells and macrophages – reticular fibres over the sinuses=> network 2 Lymph node - medulla (HE 20x) Tonsils = accumulated lymphatic tissue under the epithelium without continuous sheath function: lymphocytes production Waldayer`s circle: • tonsilla lingualis • tonsillae palatinae • tonsilla tubaria • tonsilla pharyngea Tonsilla palatina (HE 6x) Aggregates of lymphocytes&APC = lymphoid follicles of the same structure as the lymphatic nodules e.g. • Peyer`s patches • appendix - „ tonsilla abdominalis“ Spleen = the largest sec. lymphoid organ (150g) • immune filter of the blood • erythrocytes destruction • Ab production The development of the spleen • from 5th week • derived from mesenchym in dorsal mesogastrium • mesenchymal cells are differentiated in ⇒ – capsule – connective tissue net – parenchyma • in 4th month - hematopoesis • from 2nd month - white blood cells forming 3 Structure of the spleen • CAPSULE of connective tissue: – collagen fibres, some smooth muscle cells, – covered by tunica serosa (except hilum) – irradiate connective trabeculae lienalis • STROMA composed of reticular fibres • RED PULP • MARGINAL ZONE • WHITE PULP Vascularisation of the spleen elastic fib • aa. trabeculares • aa. centrales in PALS = > sinuses of the marginal zone • aa. penicillatae => splenic sinusoids - closed circulation => red pulp - open circulation • ….….venae trabeculares, vena lienalis White pulp ← PALS surrounds the central artery – T-lymphocytes ← germinal centres of the lymphatic nodule – B-lymphocytes ←marginal zone (corona) – vascular sinuses a lymphatic tissue Red pulp • splenic sinusoids – elongated endothelial cells, incoherent BM – surrounded by the reticular fibres • cords of Billroth ← lymphocytes, macrophages, reticular cells, erythrocytes .... + reticular tissue ♦ APC, B-cells Thymus = central lymphoid organ • relatively largest in birth (12-14g) • after puberty begins to involute • some remnants in adult The development of the thymus • cortical epithelial cells ← ectodermal 3th branchial cleft • medullary epithelial cells ← endodermal 3th pharyngeal pouch ♣ 10th week - colonisation by the lymphocytes ← from the blood islets, the liver and bone marrow ♣ maturation of T-cells in immunocompetent cells → into lymph nodes, spleen etc. 4 The structure of the thymus (HE 15x) • capsule → trabeculae • cortex thymi • medulla thymi The medulla of the thymus • epithelial cells of endodermic origin Cortex of the thymus • epithelial cells = star-like cells joined by desmosomes => network • many small thymocytes – mostly T-lymphocytes – many mitosis • macrophages • large T-lymphocytes Medulla (HE 480x) • thymocytes (small and medial) • fully mature T-cells • macrophages • Hassall`s corpuscles (30-150 um) The vascularisation of the thymus Histophysiology of the thymus • continuous capillaries • functional blood-thymus barrier – endothelium & basal lamina – pericytes – some connective tissue (+ macrophages) – epithelial cells • T-cells increase – carried by the blood – into nodes, spleen, Peyer` s patches etc. • in the medulla more developed than in cortex • DiGeorge syndrome - aplasia of the thymus • grow factors production proliferation a differentiation) (T-cells • corticoids and steroid hormones attenuate the proliferation, accelerate the involution 5