* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography 12
Survey
Document related concepts
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
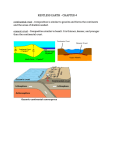
Chapter 6 Objectives: Geography 12 Worksheet 6.4 Transform Fault Boundaries: Plates Sliding Past One Another Read pages 97 – 102 of Planet Earth: A Physical Geography. Answer the following questions: Vocabulary (1 mark each) /17 Transform Faults: A fault formed by the horizontal movement of the earth’s crust, occurring where two plates are sliding past one another Normal Faults: A fault resulting from the upward movement on one side of a fault line and/or the downward movement on the other, forming a cliff or fault scarp Reverse Faults: A fault where one block of the earth’s crust moves upward against another Appreciate the power and scope of tectonic processes and their effects Appreciate the slowness of tectonic processes based on a human time scale Understand that the lithosphere is an everchanging part of a dynamic planet Understand the general pattern of tectonic activity over geologic time and explain the location pattern of tectonic activity over the earth’s surface Explain the tectonic processes that shape the earth’s surface, including folding, faulting, and volcanic activity Describe and explain the pattern of major surface features created by tectonic processes Predict the nature and general patterns of occurrence of tectonic activities and processes, especially earthquakes and volcanic eruptions Describe the positive and negative aspects of tectonic activities Fault Scarps: The often straight, continuous cliff created by the uplift of the earth’s crust along a fault line Strike-slip Faults: A fault where two sections of the earth’s crust move almost horizontally past each other Horst or Block Mountains: A steep-sided mountain formed where a block of the earth’s crust has been squeezed upward between two parallel fault lines; also known as a block mountain Tilted Block Mountain: A mountain formed where a block of the earth’s crust moves upward at an angle between two parallel fault lines Short Answer (2 marks each) 1. What causes the narrow valleys along a fault line? As the plates slide past one another, the pressures shatter the rocks along the fault line. The shattered rocks are eroded to create the valley. 2. What is fault creep? Short movements along the fault that gradually release pressure. This creep an release of pressure means earthquakes are lower in magnitude and less destructive. 3. Explain what it means when the plates are locked. What is the result then? Where the rock surfaces are rough, the plates get stuck on each other. The pressure continues to build up eventually to be released as an earthquake. The longer the pressure builds, the stronger and more destructive the earthquake. 4. Explain why the San Andreas Fault in California is worrisome to many people. Over 15 million people live in the area and since the fault is locked, scientists predict an earthquake that may cause much destruction. 5. How do laser sensors, seismographs and strain gauges help scientists detect and predict earthquakes? By measuring the movement of the earth they can determine if the fault plates are locked or creeping steadily and also measure the amount of movement of the plates. This will help them generate their predictions.