* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download why we need haptics in touch screens?
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stage monitor system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Piezoelectricity wikipedia , lookup
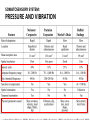
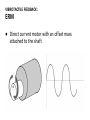
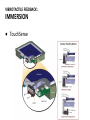
HAPTICS IN TOUCH SCREENS Heikki Säily CONTENT ● Why we need haptics in touch screens ● Somatosensory system ● Vibrotactile feedback ● Electrotactile feedback ● Summary WHY WE NEED HAPTICS IN TOUCH SCREENS? ● To provide new dimensions of usage in touch screen devices ● It can improve Human-Computer interaction ● Visually impaired ● To improve sales of product ● etc. SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM ● Can be separated to tactile and kinesthetic sense ● Technology used is usually focused on pressure and vibration SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM: PRESSURE AND VIBRATION VIBROTACTILE FEEDBACK ● Lots of different types of actuators ○ Eccentric Rotating Mass motor, or ERM ○ Piezoelectric actuator, or "piezo" ○ etc. VIBROTACTILE FEEDBACK: ERM ● Direct current motor with an offset mass attached to the shaft VIBROTACTILE FEEDBACK: ERM ● One of the most cost-effective actuator ● Vibration frequencies within 90-200hz range ● Excellent durability ● Slow does not suit well for touch sensations VIBROTACTILE FEEDBACK: PIEZOELECTRIC ACTUATOR ● Bend when voltage is applied ● When voltage is decreased, returns back to original state VIBROTACTILE FEEDBACK: PIEZOELECTRIC ACTUATOR ● Available in many different shapes, sizes, thicknesses, voltage ranges ... ● Possible to use multiple piezo actuators to provide stronger / localized haptic feedback ● Can be also used as sensors to detect vibration or pressure ● Can provide fast and short (duration 2ms) feedback ● Suitable for touch sensations ● Vibrate range from 150hz to 300hz ● Video VIBROTACTILE FEEDBACK: IMMERSION ● TouchSense ELECTROTACTILE FEEDBACK: SENSEG ● Finnish company ● Uses Coloumb's force (attraction between electrical charges) ● Tixels (Tactile pixels) ELECTROTACTILE FEEDBACK ● ● ● ● ● ● Can be generated in different ways Fairly new technology in touch screens Silent Can be integrated to displays of any shape Transparent Output and input SUMMARY ● Receptors together create sensations ● Piezoelectric actuators seem to be widely used and one can find good studies of them ● Electrotactile feedback technology is fairly new, but has great potential ● Both have their own pros and cons