* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complex Molecules
Survey
Document related concepts
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
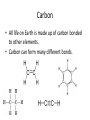
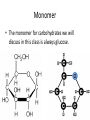
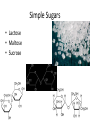
Complex Molecules 8-27-14 Warm Up: Think Ink Pair Share • What is a macromolecule? • What is a “carbon-based life form?” Carbon • All life on Earth is made up of carbon bonded to other elements. • Carbon can form many different bonds. Macromolecules • A large molecule that is composed of thousands of smaller molecules. • Monomer: one small molecule • Polymer: many monomers bonded together Macromolecules • Complex molecules needed for life. – Carbohydrates – Lipids – Nucleic Acid – Proteins Carbohydrates • Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – 1:2:1 ratio Structured Partners # of Carbon Atoms 1 4 7 2 # of Hydrogen Atoms 2 6 14 # of Oxygen Atoms 1 4 3 22 1,200 Carbohydrates • Monomer: monosaccharide • Polymer: polysaccharide • Examples of monomers Monomer • The monomer for carbohydrates we will discuss in this class is always glucose. Simple Sugars • Lactose • Maltose • Sucrose Polysaccharides Function Molecule Structure Function How it affects Humans Cellulose Glucose alternating direction Give plants structure Dietary fiber: cannot be digested Starch Chain of glucose Store sugar in plants Where humans get the majority of their energy. Glycogen Branched chain of glucose Store sugar in animals Short term storage of extra sugar. (long term converted into lipids) Simple vs. Complex • What is carb loading? • What is the difference between simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates? • Which one is better to eat? Activity • Pick one of the polysaccharides that have not been done yet. • Make a model of the molecule using colored paper. • Get filmed explaining your molecule. Closing: Think Ink Pair Share • Which is better to eat, simple sugars or complex carbohydrates?