* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (Who) is a Customer?
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Value proposition wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
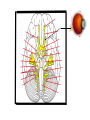
Marketing Fundamentals CUSTOMER-DRIVEN Einstein created his theories not from experiments, but from thought problems. We’re not Einstein, but this section has more to do with philosophy than practice…. It purpose is to create a mindset…. Think of two occasions when you felt that you were a valued customer. Why did you feel that way? Think of two occasions when you felt that you had a negative experience as a customer. Why did you feel that way? Fundamentals http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KkBvzS_fJ2g&feature=player_embedded# The marketing concept is the philosophy that firms should analyze the needs of their customers and then make decisions to satisfy those needs, better than the competition. Today most firms have adopted the marketing concept, but this has not always been the case. In 1776 in The Wealth of Nations, Adam Smith wrote that the needs of producers should be considered only with regard to meeting the needs of consumers. While this philosophy is consistent with the marketing concept, it would not be adopted widely until nearly 200 years later. The Production Concept Can we produce the product? Can we produce enough of it? The Sales Concept Can we sell the product? Can we charge enough for it? Examples of Marketing Concepts http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l4seWLW2KhQ&feature=player_embedded Number 1 What (Who) is a Customer? A customer? Who are we talking about? Not always clear: Who is a customer? Take a piece of paper and answer the following questions: Who is a customer? 1. Is a student a customer? Who is a customer? 1. Is a student a customer? 2. In what ways are they a customer? Who is a customer? 1. Is a student a customer? 2. In what ways are they a customer? 3. In what ways are they not a customer? Is a student a product? Is a student more like a patient? Is the student a partner? Further: Practically no one tries to sell to everyone…… Why? Because: Not everyone is a Customer! Markets are segmented: Practically no one tries to sell to everyone…… Markets are segmented: 80/20 Rule Demographics Psychographics Needs/Wants Needs are: Wants backed by resources! IS the customer always RIGHT? Is the customer always right? NO! “The cliché is wrong. The right customer is always right. The wrong customer, is not right for the selling company.” Jeffrey J. Fox Okay Customers are: Profitable Loyal Spreads positive WOM Gives positive referrals Okay customers can: also be: Tough, exacting, impatient, challenging, fickle, exasperating, needy, insistent, and a pain in the neck. Not Okay customers are: “Difficult” 1. The service provider doesn’t care about them 2. The service provider isn’t listening to them 3. The service provider isn’t doing anything to resolve the problem 4. They have been victimized, unfairly treated or taken advantage of 5. The service provider gives the customer the run-around 6. Promises are not kept Not Okay customers are: About 3% of the population is clinically insane Not Okay customers are: About 3% of the population is clinically insane Another 40% is neurotic………… And we just don’t all agree on things. http://www.expedia.com/pub/agent.dll/qscr=dspv/htid=11379/crti=7/hotel-reviews PROFITABLE Low Low High Customer Misfits Big Spenders Spinners Underachievers LOYAL Win-Back Cust Advocates New Potentials Loyalists High Student evaluation of teaching taken at random from the internet as an example. Teacher A (picked at random… named Smith) Student 1 “I am still extremely disappointed I took this class. I took it as an elective just because I thought it would be interesting... wrong teacher. The tests were so hard; I'm a straight A student and ended up with my first B. Don't take him…” Teacher A Student 2 “I like her as a person ,however, I wasn't very fond of her teaching style. The last month all we did was presentations and were left on our own. If you don't learn well this way, don't taker her. Otherwise she is pretty good.” Teacher A Student 3 “HE is a guy. His name is Roland Acosta. He's actually pretty good, but his classes take FOREVER. Bring a laptop or small GameBoy and you will be fine.” Is Teacher A: a good teacher, or a bad teacher…. Is Teacher A: For that matter: a man or a women? Types of “difficult” customers 1. Verbal abusers 2. Blamers 3. Rule Breakers 4. Opportunists 5. Returnaholics Berry, L.L, and Seiders, K. (2007) “A Cognitive-emotional Theory of Customer Injustice and Emotional Labor.” Advances in the Psychology of Justice and Affect. (D. De Cremer, Ed.), 199-226. Not Okay customers are: (bottom line) Unprofitable: i.e., not worth the price you are paying. The wrong customer is wrong. Actually…. All Businesses have Partners: Partners: Customers Competitors Employees Governments Society The Media To be successful: All of these must be kept happy! Number 2 The Importance of a Customer Orientation Clayson’s Simple Definition: “Marketing is arranging a buyer for a seller.” This means: 1. Marketing is the process of creating satisfying exchanges. 2. Wealth is created through free exchanges. Marketing Concept: “All marketing strategies should be based on known consumer needs and/or wants.” Extension: “All firms and companies have the same product… that is, a customer.” Implications………….. Managers get trapped by an inverted pyramid…. Clayson’s Even Simpler Definition: “Marketing is arranging free exchanges!” “Marketing is arranging free exchanges!” This means… 1. Marketing is the process of creating satisfying exchanges. 2. Wealth is created through free exchanges. You have a dollar…. I have a newspaper… You go into a store to buy a shirt. You go into a store to buy a shirt. What is the product? What is the promotion? What is the price? What is the place? Number 3 What are Customers Like? We like to think that our customers are like these people…. We like our customers to be upscale and aware….. http://www.uni.edu/resources/prospective-students Perception is Reality!! The right Stimulus! Getting and holding Attention! Creating the right Hypothesis! The Importance of Memory! Are Customers Rational? Depends on what is meant by rational… Depends on what is meant by rational… 1. The Theory of Utility (economics) Depends on what is meant by rational… 1. The Theory of Utility (economics) 2. The Pressure of the Environment Is a brain necessary for learning? Pavlov How much of a customer’s behavior is determined by the environment? B.F. Skinner Depends on what is meant by rational… 1. The Theory of Utility (economics) 2. The Pressure of the Environment 3. The Complication of the Psychic How much of a customer’s behavior is determined by unconscious factors? Sigmund Freud Depends on what is meant by rational… 1. The Theory of Utility (economics) 2. The Pressure of the Environment 3. The Complication of the Psychic Depends on what is meant by rational… 1. The Theory of Utility (economics) 2. The Pressure of the Environment 3. The Complication of the Psychic 4. The Subtlety of Culture How much of a customer’s behavior is determined by cultural factors? Norms Depends on what is meant by rational… 1. The Theory of Utility (economics) 2. The Pressure of the Environment 3. The Complication of the Psychic 4. The Subtlety of Culture 5. The Control of Information Marketing Maven: A maven (also mavin) is a trusted expert in a particular field, who seeks to pass knowledge on to others. The word maven comes from the Hebrew, via Yiddish, and means one who understands, based on an accumulation of knowledge. Gatekeepers… http://movies.nytimes.com/2009/12/20/movies/20scott.html Information: Example: Oliver North and Congress 1987 The Iran-Contra Affair 5/06/87 “Folks in North’s hometown recall his driving ambition” Front page story 5/06/87 (Same day) Nothing 5/08/87 North begins testimony 5/10/87 “North attracts support from sympathetic viewers.” Front page story 5/10/87 (Same day) Nothing 5/11/87 “Poll: Americans believe North but not Reagan.” Front page story 5/11/87 (Same day) “Poll: Americans believe North but not Reagan.” Front page story 5/12/87 “North comes out as hero during week of hearings” Front page story 5/12/87 (Same day) Nothing 5/19/87 “Contras sack poor village in Nicaragua: Pregnant woman, 3 kids among killed in attack” Source: NY Times Top front page story 5/19/87 (Same day) “Reagan urges more funding for Contras” On page A3 5/20/87 “Nicaragua gets more aims” [from the Soviet Union] First page story 5/20/87 (Same day) Nothing So…. What is news? Information control has become a major problem/opportunity in a connected society. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5YGc4zOqozo Number 4 What are They Actually Buying Customers do not buy products. They buy what products DO for them. What does the product do for you? What products do is not always obvious or tangible….. What a product does for one person, may not be what it does for someone else. Buyers, Users, Payers are not always the same Person. And no….that was not Sarah Palin! Number 5 How to Find Out What Customers Want/Need What is Information? Information is something that changes What You KNOW. Information is Something that Changes What You KNOW. 1. It is very valuable… and expensive. 2. It has a very pragmatic value. Information: Value Dependent upon the value of decisions that can be made with a change in what you know. Information is Something that Changes What You KNOW. 1. It is very valuable… and expensive. 2. It has a certain value. 3. The amount of information 1/prob. Information is Something that Changes What You KNOW. 1. It is very valuable… and expensive. 2. It has a certain value. 3. The amount of information 1/prob. 4. It is property. 5. It always needs to be evaluated. Information: Evaluation • • • • • • • Who produced it? When was it produced? How was it produced? How was it analyzed? Why was it produced? Who benefits from this information? Why is this information available to me? Information: Warning signs: • Confirms what you have always known. • Confirms what you WANT to believe. • Contradicts what you have always known. • Is it GOOD THINK? Number 5 Getting to Know the Customer Getting to Know the Customer How to obtain information: 1. Do marketing research… Check out: www:cba.uni.edu/clayson/mba for a complete outline for research Conflicts between MR and Management 1. Personality: The bottom line is that the manager who is using research is probably unlike the person that is producing it. 2. Research may be critical: 3. Money (expense): At times it is an expense without an explicit bottom line. 4. Time - “need it now”: Managers want information “now;” researchers want to supply it “later.” 5. Intuition (art): Successful managers typically have successful track records. Many have assumed that decision making is an “art,” and “art” and research may be seen as incompatible. 6. Past - Future Orientation: Research is ultimately done on past events, while a manager is asking for research to reduce the uncertainty about the future. 7. Pseudo Research: Researchers do not like to produce pseudo research. Managers many times want information that will never be used for decision making for a variety of reasons. Managers’ Response to Research and Evolution 1. Stage of Ignorance: 2. Stage of Blind Faith: 3. Stage of Disillusionment: 4. Stage of Sophistication: Do-It-Yourself Marketing Research Getting to Know the Customer How to obtain information: 1. Do marketing research… Check out: www:cba.uni.edu/clayson/mba for a complete outline for research 2. Start liking your customers “My job would be great if it weren’t for the customers.” Some consultants recommend that top managers spend 50 percent of their time face-to-face with actual customers. Getting to Know the Customer “Spending time with customers is a hundred times more important than attending staff meetings and reading monthly reports.” Jeffrey Fox Getting to Know the Customer How to obtain information: 1. Do marketing research… Check out: www:cba.uni.edu/clayson/mba for a complete outline for research 2. Start liking your customers 3. Listen “It does no good to get close to customers if you aren’t listening.” Jennings & Haughton Getting to Know the Customer How to obtain information: 1. Do marketing research… Check out: www:cba.uni.edu/clayson/mba for a complete outline for research 2. Start liking your customers 3. Listen Empathy Curiosity Patience Getting to Know the Customer How to obtain information: 4. Don’t be an Info-Snob “Do you do regular in-depth interviews with the sales force? Getting to Know the Customer How to obtain information: 4. Don’t be an Info-Snob. “Do you do regular in-depth interviews with the people who interact with customers (clerks, etc.)? Coast to Coast Everyone else is a “flyover.” Getting to Know the Customer “Do you do regular in-depth interviews with the sales force? “Do you do regular in-depth interviews with the people who interact with customers (clerks, etc.)? Why Not!! Number 7 Creating a Customer-Oriented Organization Product Development Don’t be product driven! Products are the objects of a transaction. It is the transaction, not the product, that is important. For example: If it is the transaction, then always make it very easy to do the transaction. Always make it easy for the customer to pay you. https://online.kitco.com/sellprice/Ordr_Faq.htm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2pkzfjnGoKo Product Development The products come from customer needs and/or wants. Products should not come from: a. What can be done b.What developers want done Product Development Don’t throw products over the wall! Destroy the Bureaucracy!! Destroy the Bureaucracy!! “Blow it up as fast as you can!” Destroy the Bureaucracy!! “Anyone found guilty of building or perpetuating bureaucracies should be tried on charges of management, malpractice, found guilty, and spend serious time in the slammer. “ Jennings & Haughton Destroy the Bureaucracy!! The best idea always win. Irrespective of where, or from whom, it comes. Destroy the Bureaucracy!! The best idea always win. Reward ideas Even when they are wrong! Destroy the Bureaucracy!! The best idea always win. Reward ideas Acknowledge people’s contributions. Positive reinforcement works almost every time it is tried. All Business is Service! “People become rich when they make other people happy. They become very wealthy when they make a lot of people happy.” Benjamin Stein The Importance of Management Management Management Management The Importance of Management Management Management Management Service is no better than management!!