* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Current / Voltage Graphs
Survey
Document related concepts
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
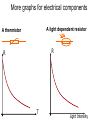
Current / Voltage Graphs These graphs allow you to predict how the component will behave when the conditions are changed. It is very important to know, since this will affect the circuit in which it is placed. You need to memorise graphs for the following… • (Ohmic) Conductors • A filament lamp • A diode • A thermistor • A light dependent resistor (LDR) An Ohmic Conductor If they are kept at a constant temperature, V/I will always give the same value. This value is equal to the RESISTANCE of the component, and is measured in Ohms (W). I (A) Reading values off the graph, then using R = V/I will give the resistance. The same value of R will be obtained from any point on the graph. V (V) A filament lamp A filament lamp does not illustrate Ohm’s law since its temperature is not constant. As a result, the resistance is not constant. I (A) Reading values off the graph, then using R = V/I will give different values of resistance from different points point on the graph. As the current through the filament increases, more heat is produced, which makes the lattice ions vibrate. This obstructs the electrons as they flow, so the V (V) resistance increases. A Diode Diodes are not metallic. They are made from semi-conducting materials. They do not always obey Ohm’s law. Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only. They can then be used to convert an alternating current to a direct current. I V More graphs for electrical components A light dependent resistor A thermistor R R T Light Intensity Thermistors and LDRs • These components are made out of semiconducting materials, so they do not behave like metals. • When given energy (like heat or light) they conduct better since more electrons become free to move through the material. • These components are used in circuits to help us to monitor and control devices automatically (like automatic night lights).