* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Survey
Document related concepts
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
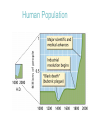
Sept. 28 & Nov. 9-10 2013 Free National parks Day! Aztec Ruins National Monument Bandelier National Monument Capulin Volcano National Monument Carlsbad Caverns National Park Chaco Culture National Historical Park El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro National Historic Trail El Malpais National Monument El Morro National Monument Fort Union National Monument Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument Northern Rio Grande National Heritage Area Old Spanish National Historic Trail Pecos National Historical Park Petroglyph National Monument Salinas Pueblo Missions National Monument Santa Fe National Historic Trail White Sands National Monument Ecology ECOLOGY – the study of how organisms interact with one another and with their environment (Eco=“house”) HABITAT – the place where a particular population of species lives NICHE- the role or “job position” that an organism has in its environment COMMUNITY-the many different species that live together in a habitat Ecosystem – a community and all the physical aspects of its habitat • ABIOTIC – nonliving component or physical factors ( minerals, rainfall, sunlight, humidity, wind temperature) • BIOTIC – living components (all organisms) ECOLOGICAL ORGANIZATION (from smallest to largest) • INDIVIDUAL – individual organisms • POPULATION – organisms of same species in same area (biotic factors) • COMMUNITY – several populations in same area (biotic factors) • ECOSYSTEM – community plus abiotic factors • BIOSPHERE – all ecosystems on Earth Food Chain-pathway of energy transfer through the feeding patterns of organisms spinach caterpillar robin garden snake owl • Producer (Photosynthetic) • Primary Consumer (Herbivore) • Secondary Consumer ( Carnivore) • Tertiary Consumer (Carnivore) • Top Order Consumer (Carnivore) • Decomposers – consume dead and decaying remains of organisms Food Web-a diagram that shows the feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem Types of Species Interactions • Predation – one benefits, other killed (cat eats mouse) • Symbiosis - two or more species live together in a close relationship Types: 1. Mutualism – both benefit (ants and aphids) 2. Commensalism – one benefits, other neither harmed or helped (clown fish & sea anemone) 3. Parasitism – one benefits, one harmed but not killed (Mistel Toe on juniper) Predator - Prey Relationship Nutrient Cycling in Ecosystems Nutrients (C, N) and water cycle through ecosystems Ex: Nitrogen Cycle Ex: carbon cycle Energy Flow In Ecosystems •Energy Flows Through Ecosystems Ex: Energy Pyramids Trophic Levels- one of the steps in a food chain or food pyramid Ten Percent Rule: 10% of the energy is used or transformed, 90% is lost as heat Growth Curves Human Population Succession-the regular progression of species replacement in the environment Succession after the 1988 Yellowstone National Park Fire Natural Succession of a Pond pond bog woodland