* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “Switch-On” Electronics - Cleveland State University
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
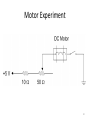
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
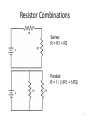
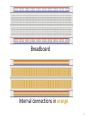
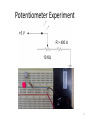
Electronics Dan Simon Cleveland State University ESC 120 Revised August 28, 2010 Voltage • Voltage is the amount of work needed to move an electric charge • High voltage in an electrical system is like high pressure in a hydraulic system • Common outlets in the United States: 120 Volts, 60 Hertz, alternating current (AC) 2 Current • Electric current: The flow of electric charge (electrons), measured in Amperes • One amp of current means a flow of one Coulomb (6.241 × 1018 electrons) per second Amps = Coulombs / second • High current in an electrical system is like high rate of flow in a hydraulic system 3 Power • Power: The rate at which current flows, measured in Watts • Power is the product of voltage and current Watts = Volts × Amps • Typical power consumption Air conditioner: 2000 W Clock: 2 W Television: 200 W Light bulb: 100 W Ohio’s average electricity cost: 12 cents per kW-hr 4 Resistors A resistor reduces the rate of flow of electric current, measured in Ohms: V = IR Example: If R1 > R2, then the current through R1 will be less than the current through R2 5 Resistor Combinations Series: R = R1 + R2 Parallel: R = 1 / (1/R1 + 1/R2) 6 7 Potentiometer Trimpot Adjuster 8 Capacitors Capacitors store electrical energy 9 Transistors Transistors can be used as electrically-controlled switches. The current through the transistor is proportional to the voltage applied to the base. 10 Diodes Diodes allow current to flow only in one direction. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) emit light. The long lead connects to the positive voltage. Current flow 11 Solderless Breadboard 12 Breadboard Internal connections in orange 13 Wire and Wire Strippers 14 Multimeter Measures voltage, current, and resistance. If you get unpredictable readings, check the battery! 15 Power Supply Regulated 5 Volt power supply: “wall wart” You need to cut off the connector so that you can connect the bare wires to your breadboard 16 Breadboard Breadboard with connector posts, ready for power supply connections 17 LED Experiment Resistor value should be at least 400 ohms 18 Potentiometer Experiment 19 Motor Experiment 20 Motor Experiment 21