* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit IV: The Grandeur That Was Rome
Roman infantry tactics wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the mid-Republic wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
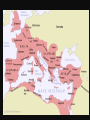
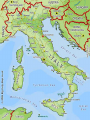
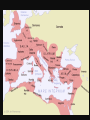
Unit IV: The Grandeur That Was Rome • Outcome 4.1: Students should be able to • Explain the geographic factors which influenced developments in the Italian peninsula. • Outcome 4.2: Students should be able to • Identify the factors which explain Rome's success in extending its control over the Italian peninsula and subsequently the Mediterranean world. ROME – QUIZ #1 • Identify the factors which explain Rome's success in extending its control over the Italian peninsula and subsequently the Mediterranean world. 4 Key Factors 1. 2. 3. 4. Geographic Economic/The Punic Wars Political/Social Military/The Punic Wars I. Geographic Factors • Mountains to the north and east initially protect the city from invasion, as does the Mediterranean sea. • Hills around Rome include rivers= fresh water • Strategically located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea • As the city grows, colonies are founded – where? • Large supply of volcanic ash and limestone to make a type of concrete for building • More forest area than Greece = good for building II. Economic Factors • As the city grows, cannot produce enough food to supply itself – must secure trade routes at sea! • Punic Wars with Carthage – Carthage controlled Sicily and had a large navy which threatened trade in the Mediterranean (as well as the potential to invade Italy III. Political/Social Factors • Influences from Greeks and Etruscans • Established a Republic following defeat of the Etruscans – unwilling to allow themselves to be ruled by another group – will of the populace. • Rome made peace with conquered peoples and allowed them to keep local customs and most land. Conquered peoples given citizenship – became Romans. IV. Military Factors • With the defeat of Carthage came compulsory military service for some • Professionalization of Army after Punic Wars – paid soldiers. • Army becomes huge – soldiering becomes a profession – army is an instrument of the state • Allowed Romans to control the Italian Peninsula and eventually the Mediterranean world • Punic Wars victory solidified Roman control over the Western Mediterranean The Second Punic War • • From Spain he marched 40,000 infantry, 8000 cavalry, & 60 battle elephants over the Alps (mountain barrier to Italy). Within two months he conquered all of Northern Italy. The Second Punic War • • Once in Italy he was almost unstoppable. He defeated the Romans at the Trebia River, & Lake Trasimene. Hannibal vs. Fabius • Rome turns to a military leader name Fabius • Fabius was asked to become dictator – Romans called him "The Delayer” – eventually removed him from power • Believed that Hannibal lacked equipment for a prolonged siege and any delay would hurt the Carthaginian food supply. • Fabius’s methods were too slow for the majority of Romans. • 2 consuls replaced Fabius—bad military leaders (Paulus and Varro) – sent 80 000 soldiers against Hannibal--vastly outnumbering the Carthaginian army – Hannibal had a force of 40,000 infantry and 10,000 cavalry The Battle of Cannae • • In Southern Italy he defeated the Romans at the Battle of Cannae. Cannae Video Battle of Cannae • • • It was a brilliant strategy of false retreat followed by attack & conquer. Roman losses: 55,000 killed including 80 senators and Consul Paulus, 10,000 captured. Hannibal loses fewer than 6,000 Rome Fights Back • Before attacking Rome he needed reinforcements. • He sent his brother, Hasdrubal. • The Romans intercepted his messengers. • After learning the location of his armies they crushed them & delivered Hastrubal's head to Hannibal. The Second Punic War • • • • Hannibal was at Rome's doorstep without siege equipment, or reinforcements from Spain. In Spain the Carthaginians were losing a counter invasion led by the Roman General Scipio. Scipio conquered all of Spain and Hannibal retreated to protect Carthage. In spite of winning every battle he lost the war. The Second Punic War • He was defeated at the battle of Zama by Scipio. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N9cqlx5CkCk&feature=related • Carthage surrendered and Rome secured the western Mediterranean • Hannibal committed suicide when assassins followed him into exile. The Second Punic War • • • • • Four reasons Hannibal lost the war: 1) No siege equipment for Rome's walls 2) Rome's allies were too loyal to join him 3) Carthage didn't get reinforcements through 4) The Romans never gave up 3rd Punic War 149-146 BC • 200-150 BC, Carthage recovered prosperity through commerce, but still militarily weak. • Romans fear revival of Carthage; demand they move inland from the coast of Africa • The Roman Senate declared war, and Rome attacked the city itself. After a siege, the Romans stormed the town and the army went from house to house slaughtering the inhabitants. • Carthaginians who weren't killed were sold into slavery. The harbor and the city was demolished, and all the surrounding countryside was sown with salt in order to render it uninhabitable. The Punic Wars -- Results 1. Rome develops naval control of the Mediterranean 2. Professionalized army (year-round paid soldiers) 3. Need for strategic military commanders to maintain dominance of expanding lands (Scipio needed to defeat Hannibal) 4. More tax income and resources generated from expanded territory The Punic Wars -- Results 1. Soldiers need retirement funds and lands 2. Rise of the military commanders who will look after their men = more success for commander = better legions 3. Powerful military leaders arise: Marius, Sulla, Crassus, Pompey, Caesar 4. Power shift from loyalty to the state to loyalty to one’s commander 5. Powerful Generals use this to their advantage