* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Analog Electronics and Communication lab
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
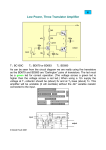
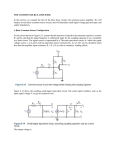
Analog Electronics and Communication lab Viva Questions and Answers 1. State maximum power transfer theorem. Maximum power is delivered from a source to a load when the load resistance is equal to the source resistance, assuming that the load resistance is a variable. 2. Define Resonance Resonance is defined as a phenomenon in an AC circuit where applied voltage and resulting current are in phase with each other. 3. List the types of resonance Series Resonance and parallel resonance 4. What is bandwidth? A range of frequencies which is occupied by a modulated carrier wave, which is assigned to a service, or over which a device can operate. 5. what is filter ? filter can be defined as an electrical network with an ability to discriminate between the frequencies, which passes certain band of frequencies while rejects remaining frequencies. 6. What is pass band ? The range of frequencies over which the attenuation provided by a filter is zero is know as pass band. 7. What is stop band ? The range of frequencies over which the attenuation provided by a filter is infinite is known as stop band. 8. What is cut-off-frequencies ? The frequencies which separates the pass band and stop band are called cut -offfrequencies. 9. What is modulation? modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform called the carrier signal with a modulating signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. 10. What is amplitude modulation? It is defined as system of modulation in which the instantaneous value of the carrier amplitude changes in accordance with the amplitude if the modulating signal 11. What is demodulation? The circuit accepts a modulated signal and recovers the original modulating information. 12. Define RPS? Regulated power supply is an electronics circuit that is designed to provide a constant DC voltage of predetermined value across load terminals irrespective of AC mains fluctuations or load variations. 13. What is rectifier? It is the process of conversion of alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC) 14. Define voltage regulator? A voltage regulator is a device designed to maintain the output voltage power supply nearly constant. 15. What is operational amplifier (OPAMP)? An operational amplifier is a direct coupled high gain amplifier consisting of one or more differential amplifiers and followed by a level translator and an output stage. 16. What is inverting amplifier? The out[put gain of the amplifier becomes negative . the result of this is that the signal is “out-of-phase” with the input signal. 17. What is non inverting amplifier? The output gain of the amplifier becomes positive . the result of this is that the signal is “in-phase” with the input signal. 18. What is clipper? It is an electronic circuit to remove some part of the input signal (clip OFF). 19. List general categories of clippers? Series and parallel (or shunt). 20. Define positive diode clipper? In a positive clipper, the positive half cycles of the input voltage will be removed. 21. Define negative diode clipper? In a positive clipper, the negative half cycles of the input voltage will be removed. 22. Define clampers? A clamp circuit adds the positive or negative DC component to the input signal so as to push it either on the positive or negative side. 23. Define slew rate? It is defined as the maximum rate of change of output voltage per unit of time under large signal conditions and is expressed in volts/secs. 24. Define input bias current? It is the average of the current entering the input terminals of a balanced amplifier 25. Define gain? It is the ratio of the output voltage to the average input voltage.