* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Data Communication Network
Survey
Document related concepts
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Routing in delay-tolerant networking wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
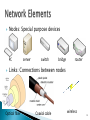
333: DISCUSS THE FUNDAMENTALS OF NETWORKING 1. Discuss networking concepts (20 hrs) 2. Discuss hardware & software requirement to setup a Local Area Network (20 hrs) PERFORMANCE STANDARD Objectives: ◦ Given a scenario, identify correctly the hardware and services required for a Network ◦ Define a Node/Host ◦ Discuss functional & geographical relationship among nodes ◦ Discuss services provided by a common carrier such as Leased line Switched line ◦ Describe switching techniques Circuit Message Packet ◦ Discuss ISO/OSl reference model ◦ Explain network communication protocols Define a Node/Host Discuss functional & geographical relationship among nodes Networking involves connecting computers and other electronic devices for the purpose of sharing information and resources and for communication A great deal of technology is required for one device to connect and communicate with another, and many choices for physical connections and related software are possible An elementary network consists of two computers connected by some kind of transmission medium Motivation: need to share data and to communicate quickly and efficiently ◦ Sharing enables users to exchange information and route data between them as workflow demands ◦ Can improve human communication substantially ◦ Peripheral device sharing enables users to take advantage of peripherals and other devices attached directly to a network or to a generally available computer attached to a network 8 9 In communication networks, a node is a connection point, either a redistribution point or a communication endpoint. A node can be a computer, printer, or other device capable of sending and/or receiving data generated by other nodes on the network. If the network in question is the Internet or an Intranet, many physical network nodes are host computers, also known as Internet nodes, identified by an IP address, and all hosts are physical network nodes. However, some datalink layer devices such as switches, bridges and WLAN access points do not have an IP host address (except sometimes for administrative purposes), and are not considered to be Internet nodes or hosts, but as physical network nodes and LAN nodes Nodes: Special purpose devices PC server switch bridge router Links: Connections between nodes Optical fiber Coaxial cable wireless 12 The task of connecting nodes via links, so that nodes can exchange information, reliably, timely, efficiently, safely, privately, “greenly”, and with low cost. Need to define the network architecture, protocols, applications, interfaces, policies, usages. A network host is a computer connected to a computer network. A network host may offer information resources, services, and applications to users or other nodes on the network. A network host is a network node that is assigned a network layer host address. Computers participating in networks that use the Internet Protocol Suite may also be called IP hosts. Specifically, computers participating in the Internet are called Internet hosts, sometimes Internet nodes. Internet hosts and other IP hosts have one or more IP addresses assigned to their network interfaces. The addresses are configured either manually by an administrator, automatically at start-up by means of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), or by stateless address auto configuration methods. Question?