* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Encoding time in fear memories
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Difference due to memory wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Reconstructive memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
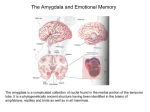
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
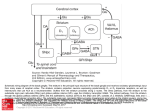
PROGRAMMEDESTAGED’INITIATIONALARECHERCHE AU1ERCYCLE SIRI UniversitédeLyon/Universitéd’Ottawa Appelàcandidature2017 Title Encodingtimeinfearmemories SurnameMOULY Supervisor-s FirstNameAnne-Marie [email protected] Phone+33(0)437287493 Institute Lab Context Abstract/Objectives SurnamePEYRON FirstNameChristelle [email protected] Phone+33(0)478771042 LyonNeuroscienceResearchCenter, CNRSUMR5292-INSERMU1028-UniversitéLyon1 https://crnl.univ-lyon1.fr/index.php/en/Research/CRNL-teams-20162020 TeamCMO https://crnl.univ-lyon1.fr/index.php/en/Research/CRNL-teams-20162020/19 TeamSLEEP https://crnl.univ-lyon1.fr/index.php/en/Research/CRNL-teams-20162020/17 How fear memories are formed and retrieved remains one of the most important questions in neuroscience, in part because stress and anxiety pathologies are continuously increasing in our modern society. In animals, fear memories can be assessed through a very popular paradigm,fearconditioning.Inthistask,asensorystimulus(forexample anodor)ispresentedtotheanimalandafterafixedinterval(ex.20sec)a mild footshock is delivered. After a few such associations, the sensory stimulus alone induces a typical fear response characterized by freezing behavior. Importantly in this paradigm, the duration of the interval between the stimulus and the footshock is fixed and it has been shown that time is learned extremely rapidly, from even single experiences. The extraction of interval duration is therefore a fundamental property of learning (Gallistel and Balsam, 2014) and allows the organism to anticipatetheproductionofanadaptedresponsetoafrighteningevent. The aim of the current project is to better understand the neural network supporting time encoding in fear conditioning in rats. Recent preliminary data from the team suggest that time encoding involves interactions between the amygdala and the dorsal striatum. In order to further investigate this hypothesis, we are currently seeking at inactivating the projection pathway between the amygdala and the striatum using chemogenetic tools. For this we will use the combined injection of a retrograde virus in the striatum and a virus containing a Dreadd (Whissell et al, 2016) in the amygdala, thus allowing to specificallyinactivatetheamygdalatostriatumprojectionpathway. Thetraineewillparticipateinthedifferentpartsoftheexperiment: • Adjustment of the best injection parameters (stereotaxic surgery) • Histological control of virus integration in the injected structures (histology,neuroanatomy) • Assessment of the effect of inactivation of the targeted pathway ontimeencodinginfearconditioning(behavioranalysis) Bibliography Selectedpublicationsfromtheteamonthetopic 1. Boulanger Bertolus J, Mouly AM, Sullivan RM (2016) Ecologically Relevant Neurobehavioral Assessment of the Development of Threat Learning.Learning&Memory2016Sep15;23(10):556-66. 2. Hegoburu C, Parrot S, Ferreira G, Mouly AM (2014). Differential involvement of amygdala and cortical NMDA receptors activation upon encoding in odor fear memory. Learning & Memory, 21(12):651-655. 3. ShionoyaK,HegoburuC,BrownBL,SullivanRM,DoyèreV,MoulyAM (2013). It's time to fear! Interval timing in odor fear conditioning in rats.FrontiersinBehavioralNeuroscience,2013Sep27;7:128. 4. Hegoburu C, Shionoya K, Garcia S, Messaoudi B, Thevenet M, Mouly AM (2011). The RUB cage: Respiration-Ultrasonic vocalizationsBehavior acquisition set-up for assessing emotional memory in rats. FrontiersinBehavioralNeuroscience,2011May19;5:25. 5. Hégoburu C, Sevelinges Y, Thévenet M, Gervais R, Parrot S, Mouly AM (2009). Differential dynamics of amino acid release in amygdala and olfactory cortex during odor fear acquisition as revealed with simultaneous high temporal resolution microdialysis. Learning & Memory,2009,16:687-697. Otherreferences 1. Gallistel CR, Balsam PD. Time to rethink the neural mechanisms of learningandmemory.NeurobiolLearnMem.2014Feb;108:136-44. 2. Whissell PD, Tohyama S, Martin LJ. The Use of DREADDs to DeconstructBehavior.FrontGenet.2016May17;7:70. Location Duration Language (French/English/Bo th) CentredeRechercheenNeurosciencesdeLyon, CNRSUMR5292-INSERMU1028-UniversitéLyon1 50AvenueTonyGarnier F-69366LYONCedex07 France 3-4months Both