* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Changes in DNA can produce Variation
Survey
Document related concepts
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
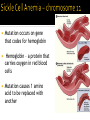
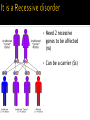
5.2 Differences or variation in DNA are what makes us different from each other! Each human cell contains 46 chromosomes Each cell has 3 billion base pairs of DNA (wow!) Our DNA is 99.99% similar Of the 6 billion base pairs of DNA, only 5% are in the genes that code for RNA and proteins. . Errors can occur when DNA is copied UV light, X-rays, chemicals, etc. affect DNA Substitution – Exchanges one base for another. CTGGAG---- CTGGGG Insertion – Extra base pairs are inserted. CTGGAG---- CTGGTGGAG Deletion- Section is lost, or deleted. CTGGAG -----CTAG Frameshift- Message is no longer read correctly. THE FAT CAT SAT --- HEF ATC ATS AT Cells have different ways to repair mistakes Certain enzymes can proofread DNA such as correcting mismatched base pairs 1. The mutation causes no effect. 1. Amino acids have more than 1 code 2. Enough protein may be produced already 2. The effect of a mutation is minor. 1. Could affect skin/eye/hair pigmentation 3. The effect of a mutation is great. 1. Genetic disorder/disease Sometimes passed from parents to offspring Sickle Cell Anemia Cystic Fibrosis (CF) Hemophilia Tay- Sachs Disease Huntington’s Disease (HD) Hypercholesterolemia Cancer Alzheimer's Emphysema Diabetes Cancer Their behavior can prevent it: Not smoking can prevent emphysema and many types of cancer Most genetic disorders cannot be cured, although progress is being made. Families who have a history of genetic disorders are recommended to undergo counseling before having a child. They can find out how it could affect their offspring. Some genetic disorders can be treated if diagnosed early enough, such as PKU (lacking a certain enzyme). If known, that child can be put on a certain diet and medicine routine. Mutation occurs on gene that codes for hemoglobin Hemoglobin – a protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells Mutation causes 1 amino acid to be replaced with another Need 2 recessive genes to be affected (ss) Can be a carrier (Ss) 5.3 Random changes in DNA can introduce new traits in an organism Humans can breed animals to get the certain traits they want. Ex: a cow that gives more quantities of milk Bloodhound – strong sense of smell The process of selecting and breeding parent organisms to pass on particular traits to the offspring. Selective Breeding A sequence of DNA from an organism is first isolated, then inserted into the DNA of another organism. The DNA inserted usually codes for a particular trait of interest GMO – Genetically modified organism Can make plants more insect resistant. Create crops suitable for areas with poor soil conditions PROS CONS Food can be resistant to certain bacteria and pests. Reduces chemical pesticides Increases food production Add nutrients Possibly harmful to the human body but still unknown Could risk wild population like salmon Can be used to produce new and better drugs for treating disease Determine the side effects of a drug on an individual Can be used to screen for and treat genetic disorders May soon allow scientists to correct certain recessive genetic disorders by replacing defective genes with copies of a healthy one. First step of gene therapy is to isolate a copy of the gene. Scientists are trying to input that gene into the cell by attaching it to a cold virus. Attempts in humans have not been successful. However, the outlook is promising. Crime scenes – skin, hair, blood DNA profile – a DNA fingerprint Everyone different except identical twins! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PwdDa6 QCDWw All the genetic material in an organism. The human genome project wanted to sequence all of the human genome (that’s a lot) We can then compare DNA across species We have similar genes to fruit flies and mice A technique that uses technology to make copies. Can be applied to a segment of DNA or a whole organism Dolly Place gene that codes for producing insulin That bacteria then replicates in large numbers Treats people with diabetes