* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Existing electrical power sources
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
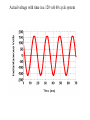
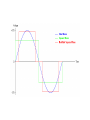
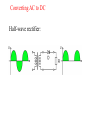
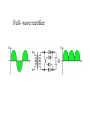
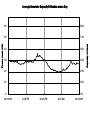
Electricity Power/Energy Basics: •In US household electricity is 120 volts AC – 60 cycles (therefore most appliances and electronic equipment require this type of current). Actual voltage with time in a 120 volt 60 cycle system Effective voltage of the AC power system is 0.707 times the peak voltage. Peak voltage is about 170 volts. Thus the 120 volts is really an effective voltage. Effective voltage is sometimes known as the rms (root mean square) voltage. Reasons for Alternating Current: •Electromechanical generators produce alternating current •Less energy loss in transmission lines if power (P) is transmitted at higher voltages (V) and lower current(I). Lower current yields less power loss (Pl). P=IxV P l = I2 x R (R = resistance in transmission line). •Voltage can be altered by transformers only for AC. For example to lower transmission voltages (e.g.,345Kv) to 120 v for household use. The frequency of generation (60 cycles per sec) is a function of the generator rotator speed. Why 60 ? Why not 50 as in Europe? Historians suggest that 60 was selected so some clocks could be synchronized with this frequency ( 60 sec/min, 60 min/hr???). Converting DC to AC Simple inverter (top = mechanical switch, bottom = transistor switch) Converting AC to DC Half-wave rectifier: Full- wave rectifier: Using capacitors and inductors we can level the voltage output of a rectifier: A capacitor opposes changes in voltage An inductor opposes changes in current. The following circuit can be used to level the voltage output A typical capacitor input filter consists of a filter capacitor C1, connected across the rectifier output, a choke L in series and another filter capacitor connected across the load. The capacitor C1 offers low reactance to the AC component of the rectifier output while it offers infinite reactance to the DC component. As a result the capacitor bypasses an appreciable amount of the AC component while the DC component continues its journey to the choke L. The choke L offers high reactance to the AC component but it offers almost zero reactance to the DC component. As a result the DC component flows through the choke while the AC component is blocked. The capacitor C2 bypasses the AC component which the choke had failed to block. As a result only the DC component appears across the load. Filtering the full-wave rectified signal using capacitors (capacitor effect indicated by red lines) yields the following output. Existing electrical power sources: 2 - 68 kW Caterpillar generators 1 - 30 kW Detroit generators Output = 480 volts 480 volts used for saltwater pump and reverse osmosis, Voltage stepped down to 120/240 for other uses. For future comparison purposes average diesel fuel consumption per capita by generators: 0.028 gal/hr (This translates to $0.20 – $0.25/kW-hr) 60 88% 50 74% 40 59% 30 44% 20 29% 10 15% 0 0% 10:15 AM 4:15 PM 10:15 PM 4:15 AM 10:15 AM Capacity Utilized Power Used (kW) Average Generator Capacity Utilization over a Day