* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Serway_PSE_quick_ch45
Survey
Document related concepts
Cold fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Inertial confinement fusion wikipedia , lookup
Inertial electrostatic confinement wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
Muon-catalyzed fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion–fission hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear drip line wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
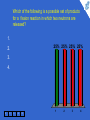
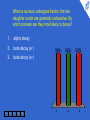
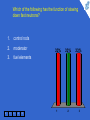
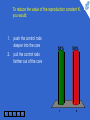
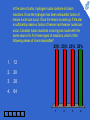
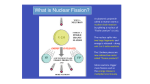
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 6e Chapter 45 - Applications of Nuclear Physics Which of the following is a possible set of products for a fission reaction in which two neutrons are released? 1. 25% 25% 25% 25% 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 This is the only set of products of the four that satisfies the conditions that the atomic numbers add to 92 and the atomic mass numbers add to 234, (allowing for two neutrons to make up the total of 236). When a nucleus undergoes fission, the two daughter nuclei are generally radioactive. By which process are they most likely to decay? 1 1. alpha decay 2. beta decay (e–) 3. beta decay (e+) 2 3 4 5 33% 1 33% 2 33% 3 According to Figure 44.4, the ratio N/Z increases with increasing Z. As a result, when a heavy nucleus fissions to two lighter nuclei, the lighter nuclei tend to have too many neutrons for the nucleus to be stable. Beta decay in which electrons are ejected decreases the number of neutrons and increases the number of protons in order to stabilize the nucleus. Which of the following has the function of slowing down fast neutrons? 1 1. control rods 2. moderator 3. fuel elements 2 3 4 5 33% 1 33% 2 33% 3 Collisions of the neutrons with moderator nuclei slow them down. To reduce the value of the reproduction constant K, you would: 1. 2. 1 2 push the control rods deeper into the core 50% 50% pull the control rods farther out of the core 3 4 5 1 2 To reduce the value of K, more neutrons need to be absorbed, so a larger volume of the control rods must be inside the reactor core. In the core of a star, hydrogen nuclei combine in fusion reactions. Once the hydrogen has been exhausted, fusion of helium nuclei can occur. Once the helium is used up, if the star is sufficiently massive, fusion of heavier and heavier nuclei can occur. Consider fusion reactions involving two nuclei with the same value of A. For these types of reactions, which of the following values of A are impossible? 25% 25% 25% 25% 1 1. 12 2. 20 3. 28 4. 64 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 Figure 44.5 shows that the curve representing the binding energy per nucleon peaks at A ≈ 60. Consequently, combining two nuclei with equal values of A > 60 results in an increase in mass, so that a fusion reaction will not occur.