* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download According to Newton`s ______ law, an object with no net force
Survey
Document related concepts
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
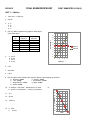
FINAL EXAM REVIEW KEY PHYSICS FIRST SEMESTER (01/2012) UNIT 1 — Motion 1. 29.2 cm/s = 0.292 m/s 2. 45 mi/h 3. a. b. c. d. C A B C 4. (P2.1C) Make a position time graph for each object in the table above. Position (m) Object A 5 5 5 5 5 5 9 Position (m) Object B 0 1 3 5 7 9 8 7 Position (m) Time (s) 0 1 2 3 4 5 10 6 5 Object A 4 Object B 3 2 1 5. a. b. c. d. 2 m/s 4 m/s 0 m/s 6 m/s 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) 6. 6.2 s 7. 420 miles 8. 0.64 s 9. (P2.2A) Which of the following are vectors? Which of the following are scalars? a. Distance scalar e. Velocity vector b. Time scalar f. Acceleration vector c. Displacement vector g. Mass scalar d. Speed scalar 11. 27 s 12. 26 m/s 13. -29.4 m/s 14. 20 15 10 5 Velocity 10. a. distance = 200 yards; displacement = 0 yards b. speed = 8.33 yards/sec; velocity = 0 yards/sec 0 -5 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 -10 15. a. 60 m b. 10 m/s2 -15 -20 Time UNIT 2 — Two-Dimensional Motion and Forces 16. a. Horizontal velocity (vx) is constant and is equal to the initial velocity in the x-direction. Vertical velocity (vy) will decrease (becoming more negative) throughout its fall. b. The direction of acceleration is straight down and equal to -9.8 m/s2. 17. The ball will fall back into the person's hand. 18. a. 444 N ┴ to the ramp b. 0 N 19. a. 381.9 N ┴ to the ramp b. 220.5 N down the ramp 20. 17.5 m 21. 0.639 s 22. Plane will be directly above the projectile UNIT 3 — Dynamics 23. Contact forces: normal force, friction force, push, pull, string force, spring force Field forces: gravitational force, magnetic force, electric force 24. Normal force is the force exerted upon an object by the surface it sits upon. The normal force is ┴ to the surface. 25. 98. N 26. a. OR b. c. 27. remains the same; 9.8 m/s2 28. backward direction 29. 429.5 N 30. Depending upon the angle, the resultant force could be between 3 N (the resultant force if angle is 180) and 17 N (the resultant force if angle is 0). If the angle is 90, the resultant force is 12.2 N. 31. For every force acting upon an object, there is an equal and opposite force acting upon a different object. 32. a. Force of book pushing down on table -- force of table pushing up on book (FN) b. Force of you pushing door open -- force of door pushing back at you c. Force of small car hitting large car -- force of large care hitting small car 33. An object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. An object in motion will stay in constantvelocity, straight line motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 34. unbalanced force 35. to the right 36. a. 588 N b. 588 N c. 498 N d. 678 N 37. c. Since the scale is accelerating downward, the net force is directed downward. This means the FN (the force the scale shows) is less than the Fg. d. Since the scale is accelerating upward, the net force is directed upward. This means the FN (the force the scale shows) is greater than the Fg 38. The sum of all the forces acting upon an object (F net) is equal to the mass of that object times its acceleration. 39. 10 N 40. 0.60 m/s2 upward 41. The mass (quantity of matter) does not change regardless of where the object is located. Weight is a function of the acceleration due to the planet's gravity, so the weight of an object will be different on different planets. 42. mass does not change 43. 245 N UNIT 4 – Momentum 44. The smaller car will experience a greater change in velocity. The car exerts the same amount of force on the truck as the truck exerts on the car (equal and opposite). Since the car has a smaller mass, it will experience a greater acceleration (v/t). 45. In a collision, the acceleration experienced by a large car is smaller than that experienced by a small car since F=ma and a large car has more mass. 46. 27.2 m/s 47. a. force would decrease b. force would increase 48. An air bag increases the "stopping time" of the passenger, decreasing the acceleration experienced by him/her. 49. 6.67 m/s 50. 8.0 m/s to right 51. 12 m/s 52. 2.67 m/s