* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid Gland
Survey
Document related concepts
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Role of skin in locomotion wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
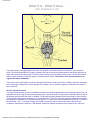
Thyroid Gland What it is - What it does... THE THYROID GLAND The thyroid gland is the biggest gland in the neck. It is situated in the anterior (front) neck below the skin and muscle layers. The thyroid gland takes the shape of a butterfly with the two wings being represented by the left and right thyroid lobes, which wrap around the trachea. The sole function of the thyroid is to make thyroid hormone. This hormone has an effect on nearly all tissues of the body where it increases cellular activity. The function of the thyroid therefore is to regulate the body's metabolism. The influence of the thyroid gland is both far-reaching and critical to normal body function. It affects heart rate, cholesterol level, body weight, energy level, muscle strength, skin condition, vision, menstrual regularity, mental state and a host of other conditions. How the Thyroid Functions The thyroid gland operates as part of a feedback mechanism involving the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. First, the hypothalamus sends a signal to the pituitary gland through a hormone called TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone). When the pituitary gland receives this signal, it releases TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) to the thyroid gland. Upon receiving TSH, the thyroid responds by releasing two of its own hormones, T4 and T3, which then enter the bloodstream and affect the metabolism of the heart, liver, muscle and other organs. T4 is the main hormone released by the thyroid. T3 is made in the tissue after T4 to T3 conversion. Finally, the pituitary "monitors" the level of thyroid hormone in the blood and increases or decreases the amount of TSH released, which then changes the amount of thyroid hormone in the blood. http://www.jctonic.com/email/SOS_02_07_2004/thyroid_pdf.html (1 of 2) [3/23/2005 5:31:02 PM] Thyroid Gland LICORICE ROOT Licorice Root is a stimulant for the adrenal glands which are controlled by the thyroid and pituitary, and which control pancreatic functions. It is good for impotency, hypoglycemia, female complaints (is a natural source of the female hormone Estrogen), endurance, coughs, constipation, colds, voice, age spots, vitality, tonic, sore throat, and as a tonic for sex stimulants. It has a dramatically beneficial effect on the adrenal glands, and is one of the best herbs used to treat hemorrhoids. It is useful in bronchitis and gastric ulcers. It is also helpful in stress. Daniel B. Mowrey, Ph.D. in his book, The Scientific Validation of Herbal Medicine, repeatedly discussed Licorice as effective for “respiratory ailments, skin conditions, as a female tonic, blood purification and detoxification, circulation, fatigue, weight loss, environmental related conditions, thyroid, whole body and mental alertness”. FDA has permitted claims that Licorice provides “soothing benefits for the stomach, digestive tract, and as an antioxidant”; “botanical support for gastrointestinal, liver and respiratory function”; a “digestive herb which benefits and soothes the stomach”; and “scientific research indicates its soothing benefits for the stomach, digestive tract, and as an antioxidant.” IODINE Iodine is a trace element that is vital to the health of the thyroid gland. Iodine provides the building blocks for the hormones secreted by the thyroid; without it the thyroid cannot function properly therefore leading to abnormal metabolism, oxygen consumption and energy production. Thyroid hormones are vital for growth and development of all organs, especially the brain, reproductive organs, nerves, bones, skin, hair, nails and teeth. The thyroid is involved in protein manufacture, cholesterol synthesis, carbohydrate absorption and the conversion of carotene to vitamin A. http://www.jctonic.com/email/SOS_02_07_2004/thyroid_pdf.html (2 of 2) [3/23/2005 5:31:02 PM]