* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Traits and probability
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
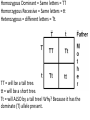
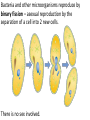
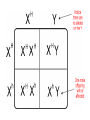
Traits and probability 6.5 Essential Question: How is a Punnett square used to predict inheritance patterns. A Punnett square is a grid system used to predict all possible genotypes resulting from a cross. Probability – the likelihood that a particular event will occur. Monohybrid cross – a cross that examines the inheritance of only ONE specific trait. T is a dominant trait for tallness. t is a recessive trait for shortness. Homozygous Dominant = Same letters = TT Homorzygous Recessive = Same letters = tt Heterozygous = different letters = Tt. TT = will be a tall tree. tt = will be a short tree. Tt = will ALSO by a tall tree! Why? Because it has the dominate (T) allele present. Dihybrid Cross – a cross that examines the inheritance of two different traits. Dihybrid crosses tend to result in a 9:3:3:1 ratio. Parental Group = P First generation of offspring = F1 Second generation of offspring = F2 Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment – Different traits appear to be inherited separately. Bacteria and other microorganisms reproduce by binary fission – asexual reproduction by the separation of a cell into 2 new cells. There is no sex involved. Multicellular organisms reproduce sexually, which means that the resulting offspring has genetic material from both parent organisms. Yes…plants can reproduce sexually… Let’s get it off so we can get it on… The advantage of sexual reproduction is that the resulting offspring is more likely to have a traits that will facilitate survival. Crossing over – the exchange of chromosome segments (DNA) between homologous chromosomes in prophase I, prophase I, PROPHASE I. Crossing over is what makes each individual human different. Crossing over is also referred to as genetic recombination. Inheritance Patterns EQ: What does it mean to have one allele that is dominant to another allele? 7.1 A carrier does not show symptoms of a disease but can pass on the allele that can cause disease to offspring. Genes that are located on the sex chromosomes (the X or Y chromosomes) are called sex-linked genes. All other genes are autosomal genes (located on autosomes). This is where it gets tricky… For sex-linked traits, males only need one copy of the allele. Females need two copies for the trait to be expressed. This is NOT good for us males… What does that mean? It means, if you’re male, you’re more likely to inherit a sex-linked trait. Incomplete Dominance – the heterozygous phenotype is in-between the homozygous phenotype (A blending of the traits). Codominance – neither allele is dominant or recessive. Pedigree charts are used to trace the genotypes and phenotypes of a family. A blue betta fish mates with another betta fish that is light green in color. Their offspring appear to have a bluish green color. What type of inheritance has taken place here? A karyotype is a picture of all of the chromosomes within a cell. Whenever a problem asks for the probability or chance of having some allele (gene), JUST go ahead and create yourself a Punnett Square. Set the square up first using the mother and father genotype. Father is usually at the top of the square. A Genotype of Hh is known as … A) Homozygous dominant B) Homozygous Recessive C) Heterozygous (carrier) Now, begin to distribute your letters DOWN each column. The letter above a square MUST go inside all of the squares below. Then, begin to distribute your letters ACROSS each row. The letter to the left of a square MUST go inside all of the squares to the right of that letter. 4 out of 4 squares have at least one capital H; all of the offspring will therefore have hairy bellies. 4/4 = 1.0 and 1.0 x 100 = 100% ¾ = .75 and .75 x 100 = 75% If a kangaroo is a carrier for large pouches, which is a dominant trait (P) and it copulates with a kangaroo that is homozygous recessive with a small pouch (p), what percentage of the offspring will have small pouches? Use a Punnett square…take 90 seconds to discuss with your group… Now…work with your group on the assignment given… Remember, NO ONE sits in the back lab area unless you have an assigned seat there. YES…that means YOU.