* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download More reactions of alkenes Objective
Survey
Document related concepts
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogenation wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
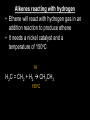
Reaction of alkenes More reactions of alkenes Objective: To know some more electrophilic reactions of alkenes Success criteria: • understand the addition reactions of alkenes with: hydrogen, in the presence of a nickel catalyst, to form an alkane halogens to produce dihalogenoalkanes steam, in the presence of an acid catalyst, to produce alcohols potassium manganate(VII), in acid conditions, to oxidise the double bond and produce a diol • understand that heterolytic bond fission of a covalent bond results in the formation of ions • understand the mechanism of the electrophilic addition reactions for the reaction of alkenes with halogens including using curly arrow notation and other given binary compounds Testing for alkenes The presence of unsaturation (a carbon– carbon double bond) can be detected using bromine water, a red/orange coloured solution of bromine. A few drops of bromine water are added to the test liquid and shaken. If a carbon–carbon double bond is present, the bromine adds across it and the solution turns colourless. 3 of 34 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 Electrophilic Addition of Br2 to Ethene • • • The same mechanism with one small difference… Br2 has an induced dipole. Draw out the mechanism – Connect the stages with just like an equation. Halgoens reacting with alkenes Halogens react with alkenes to form dihalogenalkanes • • • • Heterolytic Fission In heterolytic fission the bond breaks unevenly One of the bonded atoms receives both electrons from the bonded pair Two different substances can be formed E.g. A positively charged cation (X+) and negatively charged anion (Y-) X – Y X+ + YThe curly arrow shows the movement of an electron pair Halgoens reacting with alkenes Mechanism 1) The double bond repels the electrons in Br2 polarising Br - Br Halgoens reacting with alkenes Mechanism 2) Heterolytic (unequal) fission of Br2. The closer Br gives up the bonding electrons to the other Br and bonds to the C atom Halgoens reacting with alkenes Mechanism 3) You get a positiviely charged carbocation intermediate. The Br- now zooms over…… Halgoens reacting with alkenes Mechanism 4) ….. And bonds to the other C atom, forming 1,2-dibromoethane Halgoens reacting with alkenes But-1-ene is an alkene. Alkenes contain at least one C=C double bond. 1.Describe how bromine water can be used to test for C=C double bonds. 2.Name and draw the mechanism for involved in the above test. More reactions of alkenes Objective: To know some more electrophilic reactions of alkenes Success criteria: • understand the addition reactions of alkenes with: hydrogen, in the presence of a nickel catalyst, to form an alkane halogens to produce dihalogenoalkanes steam, in the presence of an acid catalyst, to produce alcohols potassium manganate(VII), in acid conditions, to oxidise the double bond and produce a diol • understand that heterolytic bond fission of a covalent bond results in the formation of ions • understand the mechanism of the electrophilic addition reactions for the reaction of alkenes with halogens including using curly arrow notation and other given binary compounds • • • • Alkenes reacting with hydrogen Ethene will react with hydrogen gas in an addition reaction to produce ethane It needs a nickel catalyst and a temperature of 150oC Margarine is made by “hydrogenating” unsaturated vegetable oils By removing some double bonds you raise the melting point of the oil so that it becomes solid at room temperature Alkenes reacting with hydrogen • Ethene will react with hydrogen gas in an addition reaction to produce ethene • It needs a nickel catalyst and a temperature of 150oC Ni H2C = CH2 + H2 CH3CH3 150oC • • • • Alkenes reacting with steam Alkenes can be hydrated by steam at 300oC and a pressure of 60 – 70 atm The reaction needs a solid phosphoric (V) acid catalyst The reaction is used to manufacture ethanol from ethene It is an electrophilic addition reaction and an example of a hydration reaction H3PO4 H2C = CH2 (g) + H2O (g) CH3CH2OH (g) 300oC, 60 atm Alkenes reacting with steam Mechanism Can you suggest a mechanism? Alkenes reacting with acidified potassium manganate (VII) H2C = CH2 + [O] + H2O CH2OH-CH2OH ethane-1,2-diol • If you shake an alkene with acidified potassium manganate (VII), the purple solution is decolourised (no change is observed with alkanes). • You’ve oxidised the alkene and made a diol (an alcohol with two –OH groups) • The oxidising agent is potassium manganate (VII), KMnO4, acidified with dilute H2SO4. • This is represented [O]. Questions Write the equation, and name the organic product, for the reaction between but-2-ene and: 1.Steam 2.Acidified potassium manganate (VII) More reactions of alkenes Objective: To know some more electrophilic reactions of alkenes Success criteria: • understand the addition reactions of alkenes with: hydrogen, in the presence of a nickel catalyst, to form an alkane halogens to produce dihalogenoalkanes steam, in the presence of an acid catalyst, to produce alcohols potassium manganate(VII), in acid conditions, to oxidise the double bond and produce a diol • understand that heterolytic bond fission of a covalent bond results in the formation of ions • understand the mechanism of the electrophilic addition reactions for the reaction of alkenes with halogens including using curly arrow notation and other given binary compounds Reactions of alkenes plenary What can you remember about the reactions of alkenes? Anything from the last two lessons More reactions of alkenes Objective: To know some more electrophilic reactions of alkenes Success criteria: • understand the addition reactions of alkenes with: hydrogen, in the presence of a nickel catalyst, to form an alkane halogens to produce dihalogenoalkanes steam, in the presence of an acid catalyst, to produce alcohols potassium manganate(VII), in acid conditions, to oxidise the double bond and produce a diol • understand that heterolytic bond fission of a covalent bond results in the formation of ions • understand the mechanism of the electrophilic addition reactions for the reaction of alkenes with halogens including using curly arrow notation and other given binary compounds