* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prodrug - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
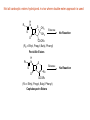
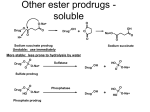
Metabolic Changes of Drugs Prof. Faris T. Abachi ( PHD Pharmacy) 3rd Year Pharmacy 2013 Hydrolytic Reactions Hydrolyzes (adds water to) esters and amides and their isosteres; the OH from water ends up on the carboxylic acid (or its isostere) and the H in the hydroxy or amine ■ ■ ■ Enzymes: Non-microsomal hydrolases; however, amide hydrolysis appears to be mediated by liver microsomal amidases, esterases, and deacylases Electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon, Nature of the heteroatom, substituents on the carbonyl carbon, and substituents on the heteroatom influnce the rate of hydrolysis In addition, Nucleophilicity of attacking species, Electronic charge, and Nature of nucleophile and its steric factors also influence the rate of hydrolysis Table: Naming carbonyl - heteroatom groups R1 R1 R2 Name Susceptibility to Hydrolysis C O Ester Highest O C S Thioester C R2 + O O Carbonate C N Amide O N Carbamate N N Ureide Lowest The Reactions O Ester hydrolysis R1 O C O R2 R1 C O Amide hydrolysis (slower) R1 C OH HO R2 O H N R2 R1 C OH H2N R2 Carbonate hydrolysis O O R1 O C O R2 R1 HO + OH Carbonate O C O HO R2 R2 HO + Carbonic acid derivative C H OH O C O + O C O + O H O H Carbonic acid Carbamate hydrolysis O O R1 O C R2 N R1 OH + HO C HN N + HO R3 R3 Carbamic acid derivative R3 Carbamate O R2 R2 C H OH Carbonic acid Urea hydrolysis R1 R2 O N C N R3 R4 Urea derivative O R1 R2 NH + HO C HN R1 C + R3 R4 Carbamic acid derivative HO C H O OH Carbonic acid O O Hydrazide hydrolysis N O R2 R3 H N N Hydrazide R2 R3 R1 C OH + H2N N R2 R3 Hydrazine C O + O H Drug Examples OH OH O OH O + O H3 C OH H3C O O Salicylic Acid Aspirin H2N H N N CH3 O CH3 Slow Hydrolysis Procainamide H2N CH3 H2 N OH O N CH3 O Rapid Hydrolysis H N N O O CH3 CH3 Procaine CH3 Lidocaine CH3 Stereoselectivity of Hydrolysis Etomidate (Amidate, hypnotic): R-(+)-isomer is more rapidly hydrolyzed, but S-(-)-isomer is more rapidly hydroxylated. The Concept of Prodrugs and Antedrugs Prodrug M D M D activation M D M D Antedrug D M D M inactivation ID M = Barrier & ID = inactive drug, D = active drug, M = modifier (I) Prodrug: Need metabolic activation (II) Antedrug: Active drug that is quickly inactivated thereby minimizing systemic effects Prodrugs and Related Terms ■ Albert in 1958 coined the term prodrug to refer a pharmacologically inactive compound that is metabolically activated in the mammalian system ■ Hard Drugs are not susceptible to metabolic or chemical transformation, have high lipid solubility and thus accumulation or high water solubility O O S F3C N NH2 O N CH3 Celecoxib: t1/2 10-12 h in humans ■ S F3C N NH2 O N Cl t1/2 ca. 680 h (Liver toxicity) Soft drugs are active compounds that after exerting its action undergo inactivation to give a nontoxic product. Indeed soft drugs are a group of modified compounds that are also designed to delivery the drugs in to the brain (the chemical delivery system). Bodor coined the term. Basic Concepts of Prodrugs ■ Carrier-linked prodrugs: a pro-moiety is attached, which is not necessary for activity but may impart some desired property to the drug, such as increased lipid or water solubility, or site-directed delivery ■ Advantages may include: ■ 1. increased absorption 2. alleviation of pain at the site of injection if the agent is given parenterally 3. elimination of an unpleasant taste associated with the drug 4. decreased toxicity 5. decreased metabolic inactivation 6. increased chemical stability 7. prolonged or shortened action Bioprecursor prodrugs contain no pro-moiety but rather rely on metabolism to introduce the functionality necessary to create an active species O OH Cl H N Cl O O2N O O O OH HO O O-Na+ O ONa O Prodrug: Chloramphenicol Hemisuccinate Na Salt O Prodrug: Prednisolon Hemisuccinate Sodium Salt ■ Inactive as it is and activated by hydrolysis by plasma esterases to chloramphenicol/ prednisolon ■ Increased water solubility for parenteral administration, which otherwise would precipitate and cause pain by damaging surrounding tissues CH 3 OH N Cl H N H3 C Cl O CH3 Cl O OH O O2N H N CH3 O HO O O Prodrug: Chloramphenicol Palmitate O S CH3 (CH2)14CH3 Prodrug: Clindamycin Palmitate ■ Inactive as it is; activated by hydrolysis by intestinal esterases to chloramphenicol/ clindamycin ■ Minimize their bitter taste and improve their palatability in pediatric liquid suspensions Prodrugs of Functional Groups Carboxylic acids and alcohols: Most common Amines and azo linkages: Not been used much Carbonyl compounds: Not found to be used widely Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols Converted to ester prodrugs which are often hydrolyzed to active drug by different types of esterase enzymes: Ester hydrolase Lipase Cholesterol esterase Acetylcholinesterase O Drug O Promoiety Drug OH + O Drug HO Promoiety Esterase or Carboxypeptidase Cholinesterase O O O Promoiety Drug OH + HO Promoiety Microflora in the gut Manipulation of steric and electronic properties of promoiety allows control of rate and extent of hydrolysis Advantage of Prodrug Formation I: Increased absorption of hydrophilic drugs by making less hydrophilic or more lipophilic H3C CH3 CH3 OH O O H3 C O H NH+ CH3 OH NH+ CH3 HO Esterase O CH3 CH3 Dipivefrin HO H Epineprine H3 C O CH3 CH3 OH Pivalic Acid Prodrug of Epinephrine: Dipivefrin More lipophilic, thus achieve higher intraocular concentration Hydrolysis occur in cornea, conjunctiva, and aqueous humor after ophthalmic application Not all carboxylic esters hydrolyzed in vivo where double ester approach is used H N R1 O S N O CH3 Esterase CH3 No Reaction COOR2 (R2 = Ethyl, Propyl, Butyl, Phenyl) Penicillin Esters H N R1 S Esterase O N O R3 COOR2 (R2 = Ethyl, Propyl, Butyl, Phenyl) Cephalosporin Esters No Reaction