* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download db2_migrate
Survey
Document related concepts
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
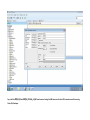
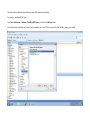
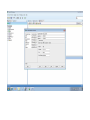
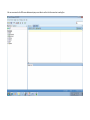
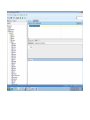
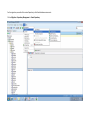
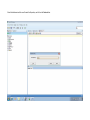
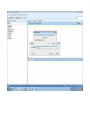
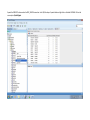
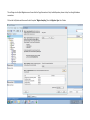
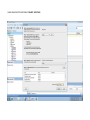
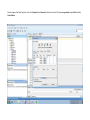
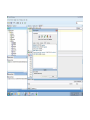
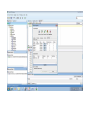
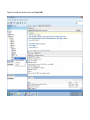
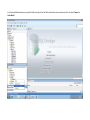
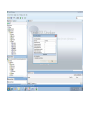
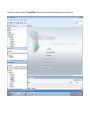
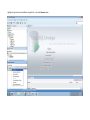
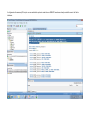
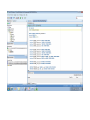
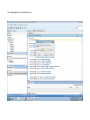
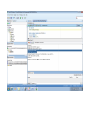
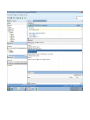
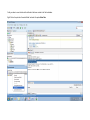
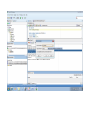
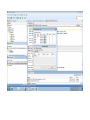
Create the user in the Oracle database. In this case we will create the DB2INST1 user – the same schema as the DB2 database. SQL> create tablespace DB2_DATA datafile '+DATA2' size 20G; Tablespace created. SQL> create user DB2INST1 identified by DB2INST1 2 default tablespace DB2_DATA 3 temporary tablespace temp 4 quota unlimited on DB2_DATA; User created. SQL> grant dba to DB2INST1; Grant succeeded. SQL> GRANT RESOURCE TO DB2INST1 WITH ADMIN OPTION; Grant succeeded. Create a connection DB2MIG connecting to the target Oracle database Cop y the files db2jcc.jar and db2jcc_license_cu.jar from the server hosting the DB2 instance to the client PC from where we will be running Oracle SQL Developer. These files will be located in the java sub-directory of the DB2 software home directory. For example - /opt/ibm/db2/V9.7/java Go to Tools > Preferences > Database > Third Party JDBC Drivers and click on the Add Entry button. Provide the location of the db2jcc.jar file which you have copied to your client PC. Do the same for the other file db2jcc_license_cu.jar as well. Create a new connection to the DB2 source database. We will need the hostname, database name, database username, password and the JDBC port number details to create the DB2 conection. In our case it is 50001. We can find the port number by issuing these DB2 CLP commands [db2inst1@blade20 ~]$ db2 get dbm cfg |grep SVCE TCP/IP Service name SSL service name (SVCENAME) = db2c_db2inst1 (SSL_SVCENAME) = [db2inst1@blade20 ~]$ cat /etc/services |grep db2c_db2inst1 db2c_db2inst1 50001/tcp We can now connect to the DB2 source database and query some tables to confirm that the connection is working fine. For the migration, we need to first create a Repository in the Oracle database environment. Click on Migration > Repository Management > Create Repository Select the database in which we will create the Repository and click on the Create button We will see that it will create a number of tables with the prefix ‘MD’ in the schema used for the repository creation. SQL> select table_name from user_tables; TABLE_NAME -----------------------------MD_TABLESPACES MD_USER_PRIVILEGES MD_REPOVERSIONS MD_USERS MD_GROUP_MEMBERS MD_CATALOGS MD_SEQUENCES MD_COLUMNS MD_CONNECTIONS MD_PROJECTS MD_MIGR_PARAMETER MD_INDEX_DETAILS MD_OTHER_OBJECTS MD_CONSTRAINTS MD_USER_DEFINED_DATA_TYPES MIGR_DATATYPE_TRANSFORM_MAP MD_GROUPS MD_ADDITIONAL_PROPERTIES MIGRLOG MD_TABLES MD_PACKAGES MD_GROUP_PRIVILEGES MD_VIEWS MD_INDEXES MIGR_DATATYPE_TRANSFORM_RULE MD_SCHEMAS MD_REGISTRY MD_DERIVATIVES MD_SYNONYMS MD_TRIGGERS MD_MIGR_DEPENDENCY MD_PRIVILEGES MIGR_GENERATION_ORDER MD_MIGR_WEAKDEP MD_CONSTRAINT_DETAILS MD_STORED_PROGRAMS MIGRATION_RESERVED_WORDS 37 rows selected. Let us now test the migration of the ACCBANK table from the DB2 database to the Oracle target database. Note the structure of the table in the DB2 source db2 => DESCRIBE SELECT * FROM ACCBANK Column Information Number of columns: 20 SQL type Type length Column name Name length -------------------- ----------- ------------------------------ ----------- 492 BIGINT 8 RECORDID 8 500 SMALLINT 2 COMPANY 7 500 SMALLINT 2 SUBCOY 6 500 SMALLINT 2 STATE 5 500 SMALLINT 2 BRANCH 6 452 CHARACTER 1 RECEIPTPF 9 496 INTEGER 4 RECEIPT 7 452 CHARACTER 1 MANRECTPF 9 496 INTEGER 4 MANRECT 7 484 DECIMAL 11, 2 CASHAMT 7 484 DECIMAL 11, 2 CHQAMT 6 484 DECIMAL 11, 2 PREVBNKAMT 10 484 DECIMAL 11, 2 CREDITAMT 9 452 CHARACTER 484 DECIMAL 452 CHARACTER 452 40 RCVDFROM 8 BANKBSB 7 20 CREDITNO 8 CHARACTER 1 CRDSYSTM 8 452 CHARACTER 2 CRDTYPE 7 452 CHARACTER 1 CRDORDER 8 452 CHARACTER 1 BANKDEP 7 6, 0 Note the number of rows in the source table db2 => SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ACCBANK 1 ----------7660 1 record(s) selected. Expand the DB2INST1 schema under the DB2_SOURCE connection in the SQL Developer. Expand tables and right click on the table ACCBANK. Click on the menu option Quick Migrate This will bring us to the Quick Migration screen. Ensure that the Target Connection in Step 2 and the Repository chosen in Step 3 are the right database connections. Click on the Verify button and then we will select the option “Migrate Everything” from the Migration Type List of Values CHANGE MIGRATION TYPE DROP DOWN TO MIGRATE EVERYTHING Note the stages of the Quick Migration – data is first Captured, then Converted to Oracle format, then DDL scripts are generated, objects Built and finally Data is Moved. Let us now see the ACCBANK table in Oracle. Note the column data type changes which have occurred. For example, the column RECORDID which was BIGINT in DB2 has now become a NUMBER column with precision 19. SQL> DESC ACCBANK Name Null? Type ----------------------------------------- -------- ---------------------------RECORDID NOT NULL NUMBER(19) COMPANY NOT NULL NUMBER(5) SUBCOY NOT NULL NUMBER(5) STATE NOT NULL NUMBER(5) BRANCH NOT NULL NUMBER(5) RECEIPTPF NOT NULL CHAR(1 CHAR) RECEIPT NOT NULL NUMBER(10) MANRECTPF NOT NULL CHAR(1 CHAR) MANRECT NOT NULL NUMBER(10) CASHAMT NOT NULL NUMBER(38) CHQAMT NOT NULL NUMBER(38) PREVBNKAMT NOT NULL NUMBER(38) CREDITAMT NOT NULL NUMBER(38) RCVDFROM NOT NULL CHAR(40 CHAR) BANKBSB NOT NULL NUMBER(38) CREDITNO NOT NULL CHAR(20 CHAR) CRDSYSTM NOT NULL CHAR(1 CHAR) CRDTYPE NOT NULL CHAR(2 CHAR) CRDORDER NOT NULL CHAR(1 CHAR) BANKDEP NOT NULL CHAR(1 CHAR) We see that the row count is the same as the DB2 database and also the indexes on the table have been created as well. SQL> SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ACCBANK; COUNT(*) ---------7660 SQL> SELECT INDEX_NAME FROM USER_INDEXES WHERE TABLE_NAME='ACCBANK'; INDEX_NAME -----------------------------CC1248759703146 Let us now see another method of doing a table migration from DB2 to Oracle using SQL Developer. In essence these are the same steps which Quick Migrate option goes through automatically, but doing in manually will give us a better overview of the entire process. Right click on the table name and select the menu option “Capture Table” Once the table has been captured, we will see in the left hand window pane, Captured Models. If we expand that it will show us the table which has been captured. In the Captured Models window pane, expand the Tables and right click on the Table name which we have captured and select the option “Convert to Oracle Model” We will now see another window pane “Converted Models” which will have all the models which have been converted to Oracle format. Highlight the particular Converted Model and right click – select the Generate option It will generate the necessary DDL scripts – we can exclude the option to create the user DB2INST1 as we have already created the user in the Oracle database. Click on Run Script icon in the SQL Worksheet tab Finally, we have to move the data to the table which has been created in the Oracle database. Right Click on the particular Converted Model and select the option Move Data

















![[Powerpoint] - DataStewardship](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003500081_1-5b11255eab8b4ea8a85021320721c6ea-150x150.png)

