* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FC Design Review II
Survey
Document related concepts
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Distributed control system wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
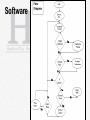
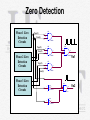
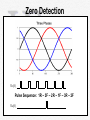
Control Why do we need system control? 1. Produce PWM 2. Synchronize AC systems 3. Control power flow 4. Protect fuel cell and interface components 5. Monitor zero crossings 6. Perform calculations How are these tasks accomplished? -DSP TMS320LF2401A TI 1. Produce PWM Seven 16-bit Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) channels which enable: - Three-phase inverter control 2. Synchronize AC Systems -Magnitude -Frequency -Phase/Zero Crossings (30 degrees ahead) 4. Protect Fuel Cell and Interface Components Checks for undesired operating conditions -Abnormal pulse width on zero crossings -Frequency variation -Voltage differences Overall System Layout -DC/DC Converter -Inverter -Transformer -Control -Software -Zero Crossing Detection DC DC DC AC Transformer :Y Control Zero-Detection Circuitry Software Interrupt Service Routine: Zero Detection • Gives a timing reference to the TI-2401 DSP on the DC/AC Inverter • Provides the ability to create a 3-phase signal synchronized with the 3-phase system on the AMPS and, ultimately, control the power flow to the AMPS Zero Detection Zero Detection Phase 1 Zero Detection Circuits Vop(1) Von(1) 3 2 74HC86 Vop(2) Von(2) Phase 2 Zero Detection Circuits U2A 1 U2B 1 2 8 6 5 9 74HC86 74HC4075 Vo1 U2C Vop(3) 9 8 10 74HC86 Von(3) Phase 3 Zero Detection Circuits U1A 4 U4A U3A 1 2 1 2 13 12 74HCT04 74A C11 U3B 3 4 74HCT04 Vo2 Zero Detection Vo1(t) Pulse Sequence: 1R – 3F – 2R – 1F – 3R – 2F Vo2(t) Zero Detection – PCB Board • • • • • 4-layer board – Signal 1, Signal 2, Vcc, GND Required external power supply: ±18V On-board linear voltage regulator: 3.3V Inputs (3): 120VAC (3-phase) Outputs (2): serial pulse stream, phase 1 (rising) ref signal • (Picture) Zero Detection - Prototype Current Budget* Item Predicted Cost Actual Expenditures DC/DC Converter $318 $398.00 DC/3-Phase AC Converter $500 $500.00 Hydrogen $45 Poster/Report Binding $35 Project Display Costs $35 Protection Circuitry $50 Filtering $50 Printed Circuit Boards $350 $180.00 Circuit Components $150 $159.96 Utility Cart $100 Miscellaneous $300 Shipping $125 $66.40 DSP Software $495.00 Donated XDS510PP-Plus Parallel Port Emulator $999.00 Donated $3,552 $866.76 Total *Funds received from Power Lab Budget and O’Conner/Corbit Fund QUESTIONS? OUTPUT Max 200W 208V ± 2% 70VLL AC 3-phase AC 3-phase Synchronous Freq. 120V DC ±1% DC DC DC AC Synchronous Freq. 70:208 Transformer :Y INPUT 18-36V DC Control Zero-Detection Circuitry