* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 MONOSTABLES A monostable circuit provides a single output
Survey
Document related concepts
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
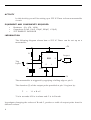
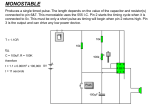
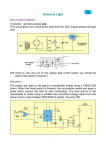
MONOSTABLES A monostable circuit provides a single output pulse (one-shot) of fixed duration when a short pulse is applied at its trigger input. T MONOSTABLE Trigger pulse Q Output pulse Fig. 1. Function of a monostable Under normal conditions, the monostable will be in a stable state with its output Q at logic level 0. When it receives a short trigger pulse, it enters an unstable state and output Q changes to logic level 1. It remains in this state for a time (T) then changes back to its stable state. The duration of T depends upon values for resistors and capacitors in the timing circuit. While in its unstable state, the monostable ignores any pulses applied at its input. It can only be re-triggered after it has returned to its stable state. Some monostable circuits are triggered by the rising edge of the trigger pulse while others are triggered by the falling edge. You will come across examples of both types in your Practical Exercise. PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS TIMERS Monostables are often used as timers e.g. to switch on a light for a fixed period of time after being triggered. PULSE STRETCHERS Logic probes are often fitted with pulse stretching circuits so that an indicator stays on for a few seconds when a very short pulse appears in a logic circuits. 1 THE 555 TIMER IC The 555 IC was the first general-purpose timer (ASIC - Application Specific Integrated Circuit)capable of both monostable and astable operation. The device is available in an 8-pin dual in line (DIL) package with pin outs shown in fig.2. Ground Trigger Output Reset 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 Fig. 2 +Vcc Discharge Threshold Control voltage The pin layout of the 555 THE 555 AS A MONOSTASBLE The 555 timer can be configured as a monostable using only 3 external components. Vcc (3 to 15 V) R 8 Output 555 7 Trig Input 4 6 3 2 5 C 1 T 10nF 0V Fig. 3 The 555 as a monostable A 10nF capacitor is connected to pin number 5 to reduce noise at the input of the comparator. 2 The trigger is active low, producing an output pulse of duration: T = 1.1 R x C It is recommended that R is in the range of 10 kΩ to 10 MΩ 100pF to 1000uF for power economy and predictability. and C in the range of Practical use: To produce a delay of 5 seconds the values of R and C must be derived. The simplest method is construct the resistor from a fixed 1kΩ and a 100kΩ variable. The fixed value limits the lower resistance. Therefore R is in the range 1 to 101 kΩ. If we assume that R is a mid value approximately 50kΩ then we are able to find a value for C T = 1.1 x R x C C = T/ ( 1.1 x R) C = 5 / ( 1.1 x 50x103) C = 9.1x10-5 F= 91µF The closest value would be a 100µF capacitor, the 100kΩ variable resistor could be adjusted to produce a 10 second delay. 3 ACTIVITY In this Activity you will be setting up a 555 IC Timer to form a monostable circuit. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS REQUIRED • • • Resistors (1k, 47k, 100k) Capacitors (10nF, 10µF, 100µF, 220µF, 470µF) 555 TIMER IC PACKAGE INFORMATION The following diagram shows how a 555 IC Timer can be set up as a monostable. +5V 8 R 4 6 Output 555 7 Trig Input 3 2 5 C 1 T 10nF 0V The monostable is triggered by applying a falling edge at pin 2. The duration (T) of the output pulse provided at pin 3 is given by: T = 1.1 x R x C T is in seconds if R is in ohms and C is in Farads. Investigate changing the values of R and C, produce a table of output pulse time for different values. 4