* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Where do elements come from?
Survey
Document related concepts
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
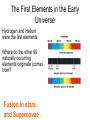
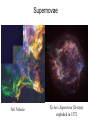
Video Questions • What elements were created during the big bang? • What elements are created as fusion in stars? • What elements are created during a super nova explosion? • How does the mass of the star effect element creation? Where do elements come from? The First Elements in the Early Universe Hydrogen and Helium were the first elements Where do the other 90 naturally occurring elements originate (come) from? Fusion in stars and Supernovae Elements in the stars as viewed from Earth Elements are made in stars • Stars are hot ionized balls of gas (plasma) full of energy and are held together by gravity • Everything is made from the elements created in massive stars. Stars are huge factories producing the elements found in the Universe. What is Nuclear Fusion? Combining of atomic nuclei • The star creates heat and light by nuclear fusion. Light Hydrogen atoms fuse into Helium atoms. Lighter Elements: Atomic # ≤ 26 • Lighter elements fuse to create heavier elements like carbon and oxygen • During the life span of a star, fusion can take place up to the formation of Iron (Fe) Supergiants What happens to the high mass stars when they exhaust their He fuel? • They have enough gravitational energy to heat up to 6 x 108 K. – C fuses into O • C is exhausted, core collapses until O fuses. • The cycle repeats itself. – O Ne Mg Si Fe © 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Heavier Elements: Atomic # > 26 Supernova Crab Nebula in Taurus supernova exploded in 1054 The amount of energy released is so great, that most of the elements heavier than Iron (Fe) are instantly created. Supernovae Veil Nebula Tycho’s Supernova (X-rays) exploded in 1572 • After a supernova, a solar nebula is formed which contains heavier elements • This nebula forms new stars with a higher concentration of heavier elements • Our Sun has 67 different elements and is thus a later generation or “recycled” star Where do elements come from? Where do elements come from? •Big Bang •Fusion in Stars HHeC… •Supernovas Recycled Matter